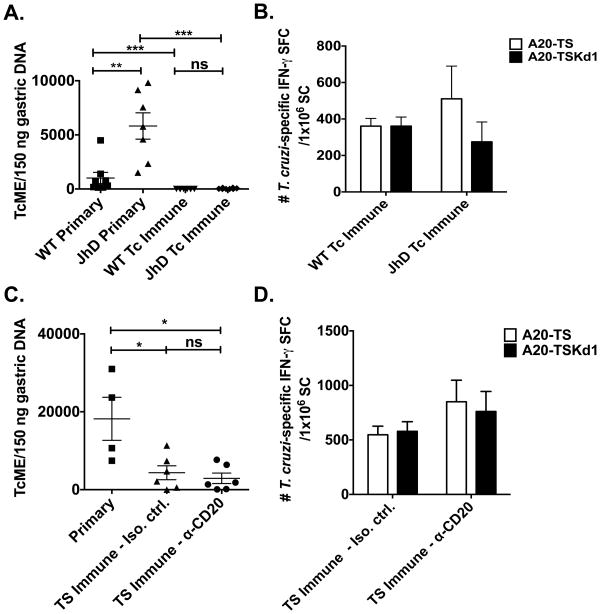
Figure 2. B cells are not required for protective mucosal T. cruzi immunity.
(A,B) Tc immune JhD B cell KO and WT BALB/c mice were generated by repeated low-dose intragastric T. cruzi infections as described in Figure 1. One month following the last intragastric infection, naïve and Tc immune B cell KO and WT mice were challenged intragastrically with a high dose T. cruzi. Twelve days later (the point at which T. cruzi DNA is highest in the gastric mucosa (17)), mice were sacrificed and (A) gastric DNA isolated to assess the level of T. cruzi DNA via qPCR. n=7-8 mice/group. Data are derived from two independent experiments pooled together. (B&D) Splenocytes (SC) were isolated and the frequency of IFN-γ-producing TS or TSKd1-specific T cells measured via ELISPOT. Background responses were subtracted from the experimental values. (C,D) Mucosal TS immune mice were generated by intranasal vaccination with recombinant TS+CpG 1826 twice, two weeks apart. Mice were either B cell depleted (α-CD20) or not (IgG1κ) starting two weeks prior to vaccination. One month after vaccination, naïve and TS immune mice were challenged intragastrically with a high dose of T. cruzi. Twelve days later, mice were sacrificed and (C) gastric DNA isolated to assess the level of T. cruzi DNA via qPCR. n=5 mice/group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.0005 Mann-Whitney U-test. TcME = T. cruzi molecular equivalents; SFC = spot forming cells. Error bars represent SEM.