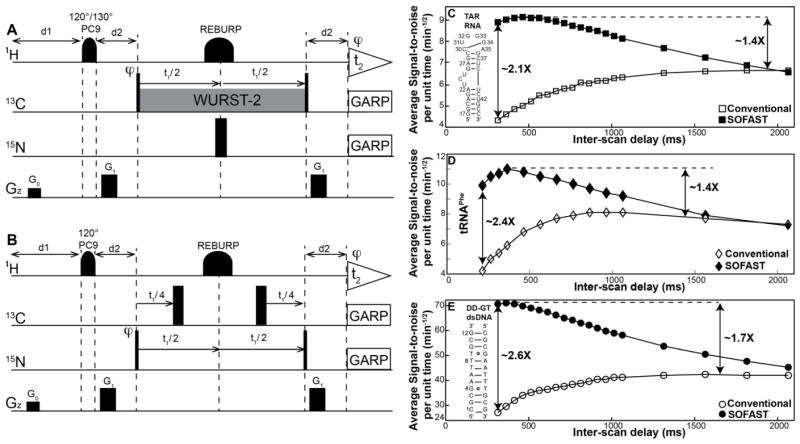
Fig 1.
(A) Pulse sequence for 2D aromatic [13C, 1H] SOFAST-HMQC for nucleic acids. (B) Pulse sequence for [15N, 1H] long-range SOFAST-HMQC experiment that correlates the two-bond N-H in purine bases of A and G. (A,B) Rectangular 90° and 180° pulses are indicated by thin and thick vertical bars, respectively, and phases are indicated above the pulses. The phase of all pulses is x unless indicated otherwise. PC9 and REBURP pulses are employed for selective excitation and refocusing of aromatic/imino protons. 120°/130° PC9 excitation pulses centered (with bandwidth) at 8.0 (±1.5 ppm) / 12.0–13.1 ppm (±2.0–3.0 ppm) are employed for aromatic/imino protons. The coherence transfer delay d2 is set to 2.5 ms corresponding to 1/(2JCH) for aromatic HMQC, while for the long-range 2D [15N, 1H] and [13C, 1H] SOFAST-HMQC experiments is optimized to 19.5 and 31.3 ms, respectively, for maximum signal intensity accounting for relaxation loses. Watergate sequence (Piotto et al. 1992) is employed with the selective 180° refocusing pulse for water suppression. Band selective WURST-2 pulses (ω1 ~1350 kHz) are used for homonuclear 13C-13C decoupling centered at 98 ppm for RNA (at 100 and 115 ppm for DNA) and at 15 and 150 ppm for the long-range [13C, 1H] experiment. Heteronuclear 13C-15N decoupling is accomplished by applying a 180° non-selective refocusing pulse is applied on the 15N channel with the carrier place at 200 and 235 ppm for aromatic and long range [13C, 1H] HMQC, respectively. Delayed acquisition (Cavanagh et al. 2006) is employed for t1-sampling, aiding in distinguishing folded peaks as they appear with opposite phase to that of regular peaks. A globally optimized alternating phase rectangular pulse (GARP) (Shaka et al. 1985) is employed to decouple 13C/15N (ω1 = 2.4/1 kHz) during signal acquisition. Pulsed z-field gradients (PFGs) are of rectangular shape, and their duration and strengths are: G0 (100 μs, 21 G/cm); G1 (600 μs, 24 G/cm). Phase cycling: φ = x, −x was employed for axial peak suppression (Cavanagh et al. 2006). Quadrature detection in t1(13C/15N) is accomplished by altering the phase φ according to States-TPPI (Cavanagh et al. 2006). Average signal-to-noise per unit time (SNt) as a function of inter-scan delay for (C) 1.0 mM uniformly 13C/15N labeled TAR RNA (D) 0.5 mM uniformly 13C/15N labeled tRNAPhe and (E) 3.0 mM uniformly 13C/15N labeled DD-GT-dsDNA from aromatic conventional (open objects) and SOFAST- (solid objects) HMQC experiments.