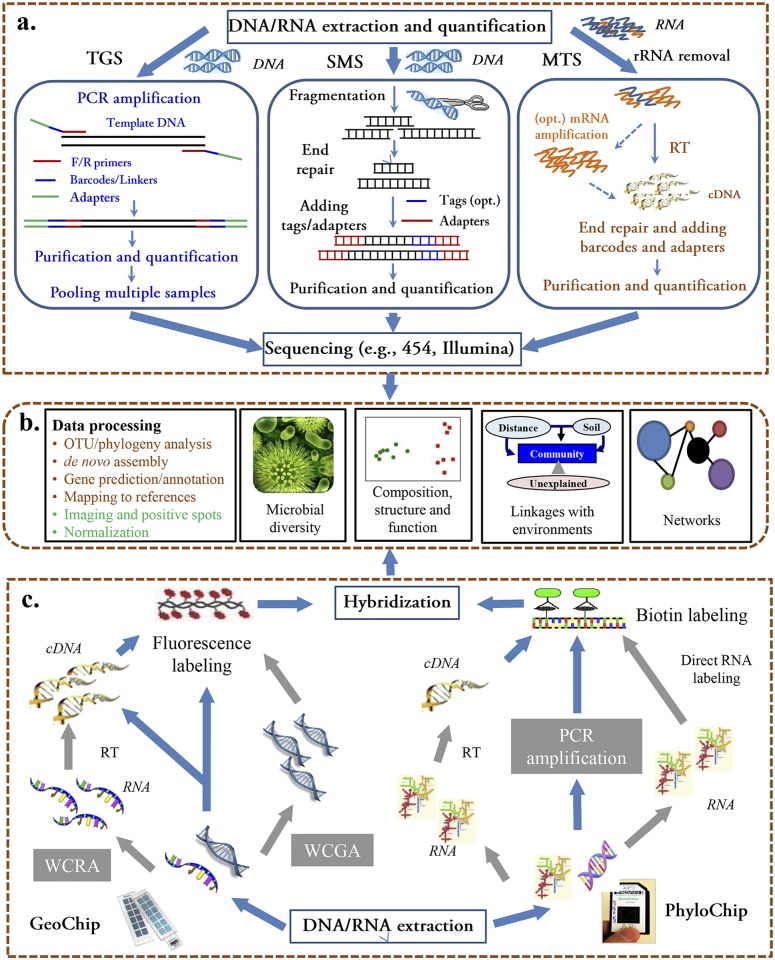
FIG 1 .
Key steps of high-throughput metaomic technologies for microbial community analysis. (a) Sequencing-based open-format technologies. Extracted DNA/RNA samples are prepared for sequencing by target gene sequencing (TGS), shotgun metagenome sequencing (SMS), and/or metatranscriptome sequencing (MTS). RT, reverse transcription. (b) Data processing and analysis. Both sequencing- and microarray-based data are processed and then statistically analyzed to address specific microbial ecology questions related to community diversity, composition, structure, function, and network, as well as their linkages with environmental factors. (c) Array-based closed-format technologies. For the GeoChip and PhyloChip, extracted DNA is directly labeled and hybridized, while RNA is first reverse transcribed (RT) to cDNA. DNA and RNA can be amplified by whole-community genome amplification (WCGA) or by whole-community RNA amplification (WCRA), respectively, when there is not enough mass for direct hybridization, but this compromises quantification. Images from both arrays are digitized for further data processing and statistical analysis.