Figure 2. Radial Arm Water Maze.
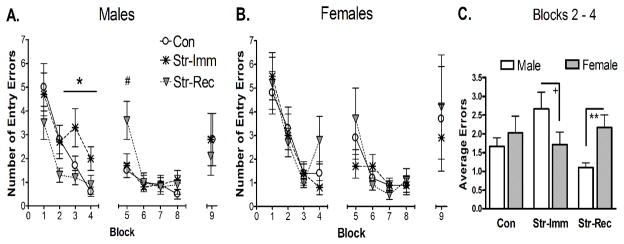
A and B. All groups demonstrated improved performance during acquisition (Day 1: blocks 1–4, Day 2: blocks 5–8). Data points represent mean entry errors ± SEM for each block. A. In males, significant acquisition effects were found on day 1. After the first block of information gathering (block 1), Str-Imm males made significantly more errors compared to both CON and Str-Rec males (* p < 0.05, blocks 2–4). Str-Rec and Con males showed statistically similar number of errors on day 1. However, at the beginning of the second day of training, Str-Rec rats made more errors than both Con and Str-Imm males (# p < 0.05, block 5), possibly indicating greater overnight forgetting. No other effects of stress history were found in males on day 2 of training (blocks 5–8) or on the retention trial (block 9). B. In females, no main effect of history was detected on any day or block. C. Sex differences were evident on day 1, blocks 2–4, where males demonstrated significant effects of stress history. Str-Rec females made significantly more errors than Str-Rec males (** p < 0.01) while Str-Imm females demonstrated a pattern of making fewer errors than Str-Imm males (+ p = 0.1). Con males and females did not differ. Bars represent mean ± SEM entry errors on blocks 2–4.
