Figure 5. TLR4 signaling negative feedback is regulated by the miR-199a-5p/CAV1 axis in an AKT-dependent manner and this pathway is altered in CF MΦs.
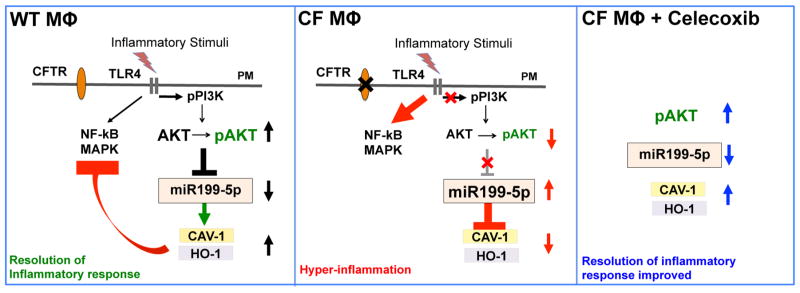
TLR4 activation induces the PI3K-AKT pathway in MΦs, which down-regulates microRNA miR-199a-5p, allowing expression of CAV-1 and subsequent negative feedback on the TLR4 pro-inflammatory cascade (NF-kB/MAPK signaling). In absence of functional CFTR, MΦs have a blunted PI3K/pAKT signaling in response to TLR4 activation, which leads to accumulation of miR-199a-5p. Increased levels of miR-199a-5p, targeting the 3′-UTR of CAV1, interfere with induction of CAV1 in response to inflammatory triggers, ultimately leading to ineffective negative feedback of TLR4 signaling and hyper-inflammation. Celecoxib stimulates the AKT/miR-199a-5p/CAV1 pathway in CF murine and human MΦs, and decreases lung hyper-inflammation in Cftr-deficient mice.
