Figure 3.
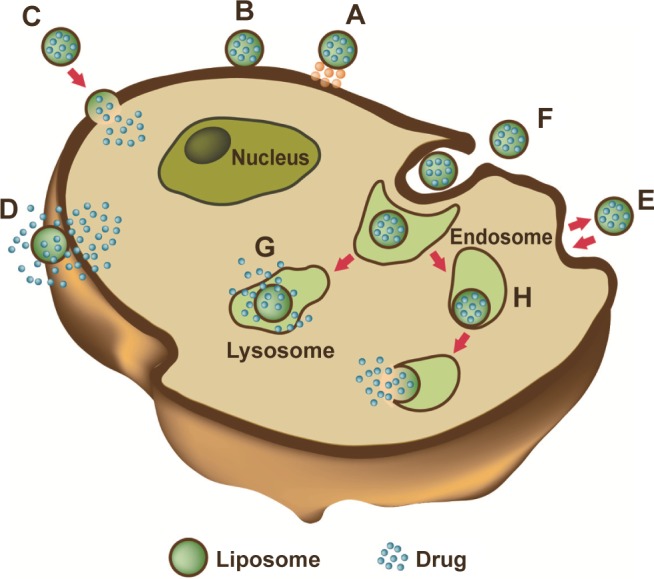
Liposome–cell interaction.
Notes: Liposomes loaded with a drug interact with the cell, binding to the surface through receptors (A). Absorption onto the plasma membrane can also occur by electrostatic interactions (B). The delivery of the cargo into the cell cytoplasm can take place through different modes. Lipid nanocarriers fuse with the plasma membrane and discharge drugs into the cell (C). After the interaction with the cell, the structure of the liposome bilayer can be affected and the cargo is released (D). Exchange of carrier-lipid components with the cell membrane can also occur (E). Liposomes internalized by endocytosis (F) can have different fates depending on physicochemical characteristics. Endosomes fuse with lysosomes (G): in this case, the low pH induces the degradation of the liposome membrane and the drug is released. Endosomes follow another route (H): liposomes release their cargo after fusion or the destabilization of the endocytic vesicle.
