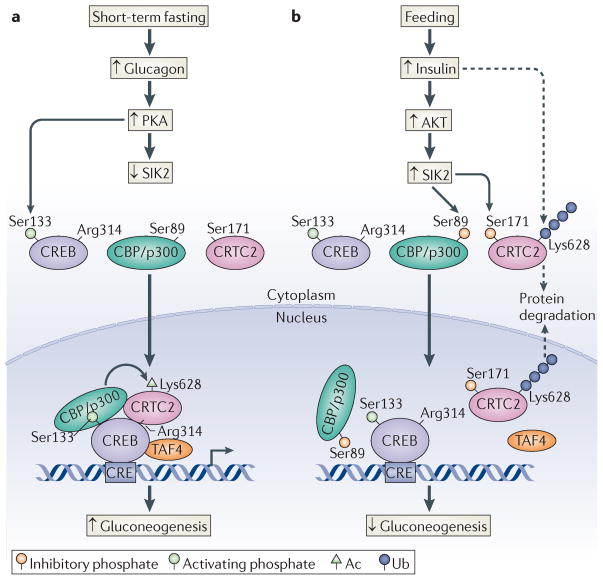
Figure 5. Glucagon and insulin antagonism.
Opposing effects of glucagon and insulin on the cyclic AMP-responsive element (CRE)-binding protein (CREB) pathway. a | Glucagon stimulates the protein kinase A (PKA)-mediated phosphorylation of CREB at Ser133. PKA also stimulates cAMP-regulated transcriptional co-activator 2 (CRTC2) activity via the phosphorylation and inhibition of salt-inducible kinase 2 (SIK2), leading to the dephosphorylation of CRTC2. Dephosphorylated CRTC2 translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to CREB and promotes the recruitment of TBP-associated factor 4 (TAF4) and CREB-binding protein (CBP) and its paralogue p300. Nuclear CRTC2 is transiently stabilized by CBP/p300-mediated acetylation (Ac) at Lys628. b | Insulin signalling stimulates AKT, which phosphorylates and activates SIK2. Active SIK2 disrupts the CRTC2–CBP/p300 interaction by phosphorylating CBP/p300 at Ser89, leading to the deacetylation and ubiquitin (Ub)-dependent degradation of CRTC2. SIK2 also promotes the cytoplasmic translocation of CRTC2 through phosphorylation at Ser171.