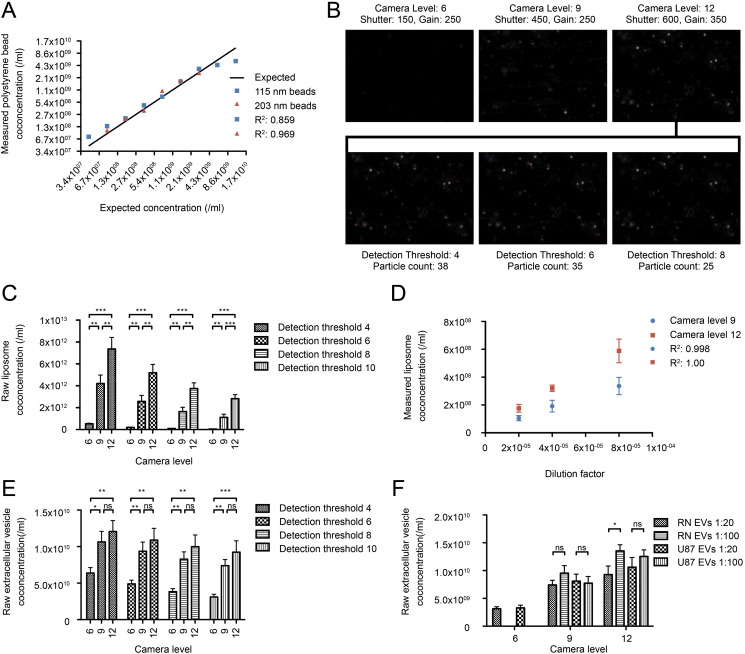
Fig. 1.
NTA-based quantification of beads, liposomes and EVs. (A) Quantification of 115 and 203 nm polystyrene beads. The measured concentration of the beads is plotted against the expected concentration based on the manufacturer's supplied stock concentration. Detection was performed at camera level 5 (shutter: 100, gain: 200) for the 115 nm beads and camera level 3 (shutter: 20, gain: 0) for the 203 nm beads. (B–D) Quantification of 115 nm-sized liposomes. The effect of camera level and detection threshold was assessed, demonstrating visual differences in particle imaging (screenshots in (B)) as well as differences in the calculation of raw concentrations (C). Dilution of liposomes showed linearity with the measured liposome concentration, at camera levels 9 and 12 (D). (E–F) Quantification of purified EVs. The effect of camera level and detection threshold on quantification of EVs (from RN cells) is shown in (E). The effect of sample dilution (1:20 and 1:100) on quantification is shown in (F), with EVs included from RN cells and U87-MG cells, and analysis at three different camera levels. Data are mean ± s.d. (n = 3).