Figure 6. Role of ILK in the EA.hy926 cell uraemic toxin-induced apoptosis.
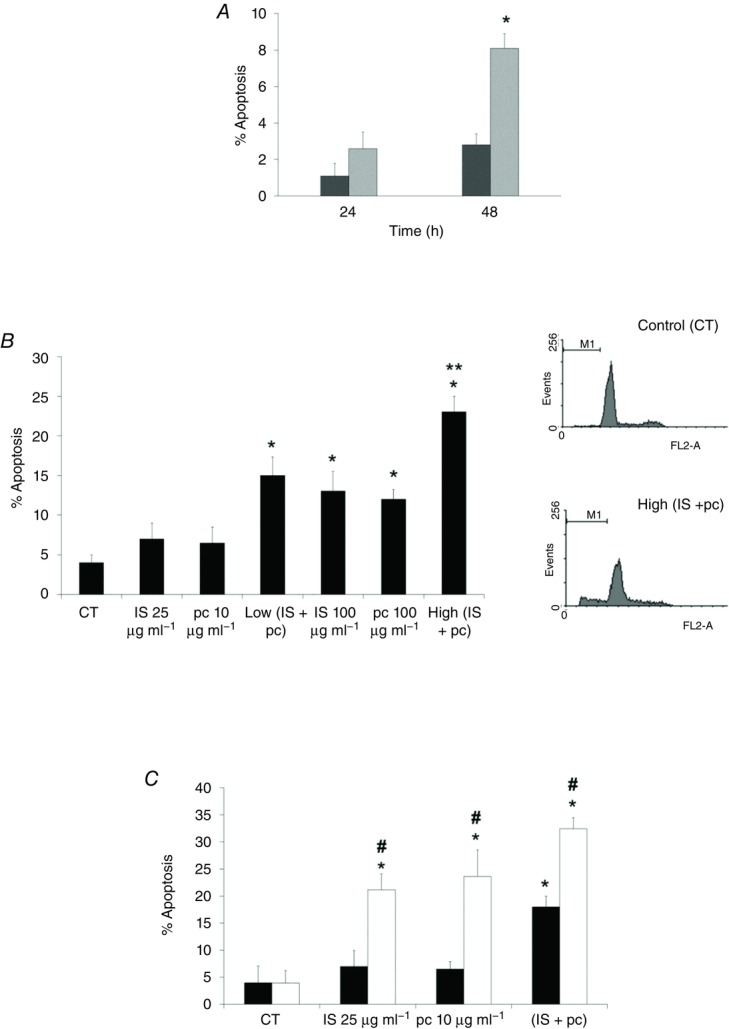
A, cells were incubated in medium supplemented with normal serum (NS, dark grey bars) (10%) or uraemic serum (light grey bars) (10%) for 24 and 48 h. B, cells were incubated in medium supplemented with 2.5% NS plus indoxyl sulfate (IS; 25 or 100 μg ml−1), p-cresol (pc; 10 or 100 μg ml−1), a combination of low concentrations of IS (25 μg ml−1) and pc (10 μg ml−1) (Low IS + pc) or plus a combination of high concentrations of IS (100 μg ml−1) and pc (100 μg ml−1) (High IS + pc) for 24 h. **P < 0.05 vs. Low (IS + pc). C, cells were depleted of ILK with specific siRNA (open bars) (100 nm) and treated afterwards with IS (25 μg ml−1), pc (10 μg ml−1) or both, for 24 h. Scrambled RNA (Sc) (filled bars) was used as control. After incubation, apoptosis was determined in PI-stained cells and analysed by flow cytometry. Representative graphs are shown. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of seven independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. control (CT; 2.5% NS, 24 h); #P < 0.05 vs. Sc.
