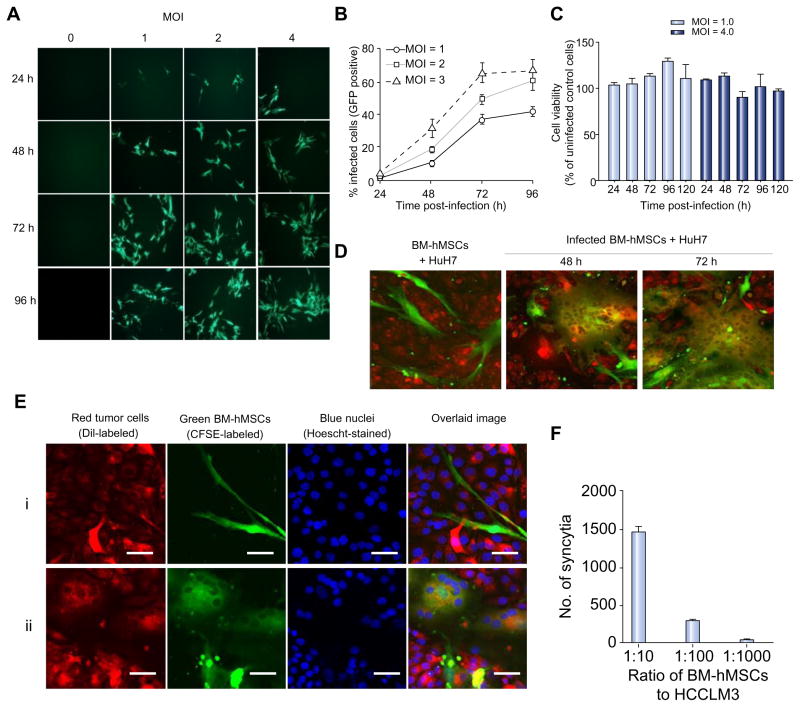
Fig. 1. MV can infect BM-hMSCs and transfer the infection to HCC cells in vitro.
(A) BM-hMSCs were infected with MV-GFP, (B) quantitated by flow cytometry for GFP-expressing cells and (C) evaluated for cell viability with MTS assay at the indicated time-points. CFSE-stained MV-infected BM-hMSCs were overlaid on DiI-labeled HuH7 cells at a 1:20 ratio. (D) At 48 and 72 hours post-overlaid, cells were photographed with a confocal microscope. (E) High-resolution analysis of heterofusion between green BM-hMSCs and red HuH7 cells resulted in observation of multinucleated yellow-colored synctia (Eii). For comparison, co-culture of uninfected BM-hMSCs (green) with HuH7 (red) did not result in heterofusion (Ei). Scale bar = 50 μm. (F) MV-induced syncytia formation increases with the number of infected BM-hMSCs. (This figure appears in colour on the web.)