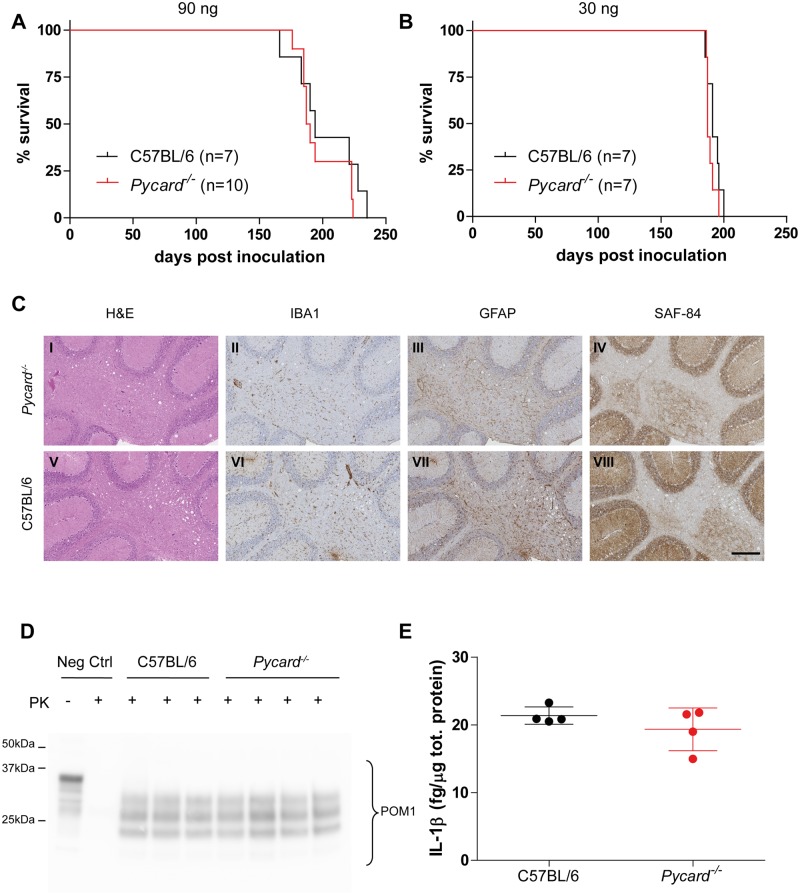
Fig 2. Prion disease in the absence of ASC.
A-B Kaplan-Meier survival plots of Pycard -/- (red line) and C57BL/6 wild-type mice (black line) inoculated intracerebrally with 90 ng (A) or 30 ng of RML6 prions (B). For each experimental group, the number of mice is indicated (n). With both doses, no statistically significant difference was observed (90 ng = median survival Pycard -/- 189 dpi, C57BL/6 194 dpi, P = 0.35; 30 ng = Pycard -/- 187 dpi, C57BL/6 191 dpi, P = 0.23, log-rank test). C Histological analysis of Pycard -/- (I-IV) and C57BL/6 wild-type mice (V-VIII). Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) and immunohistochemical stainings for microglia (IBA1), astrocytes (GFAP) and partially protease-resistant PrP (SAF-84) in cerebellar areas are displayed. Scale bar: 250 µm. D Western blotting analysis of partially protease K (PK)-resistant PrP as detected with POM1 in brain homogenates after PK digestion (PK +). Neg Ctrl: brain homogenate from a control mouse not inoculated with prions is shown with (PK +) and without (PK -) PK digestion. E Levels of IL-1β in brains of terminally sick mice. Each point denotes one mouse. Mean +/- standard deviation are shown. No significant difference was observed (P = 0.28, Student’s t test). C, D and E are referred to mice inoculated with 30 ng of RML6.