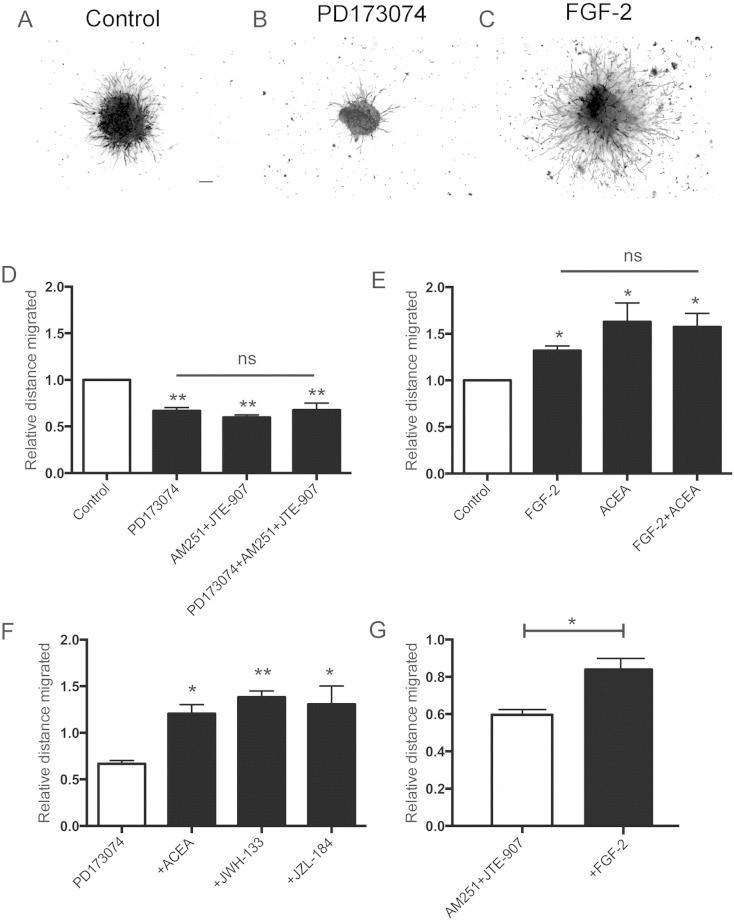
Fig. 7.
FGF and eCB signalling can operate independently in culture.
RMS explants isolated from P5–P8 mouse brains were embedded in Matrigel and left to migrate for either 6 h or 24 h before fixation. Representative pictures of explants stained with phalloidin treated with vehicle (A), 1 μM of the FGFR inhibitor PD173074, (B) or 2 ng/ml FGF-2 (C) taken 24 h after embedding. In the 6 h assay, treatment with 1 μM PD173074 significantly decreased migration to the same extent observed after incubation with the CB1/2 antagonists AM251 and JTE-907 (0.5 μM each) (D). When FGFR and CB receptors were inhibited simultaneously, there was no further significant decrease in migration (D). In the 24 h assay FGF-2 (2 ng/ml) significantly promoted migration to the same level observed after incubation with the CB1 agonist ACEA (0.5 μM), and treatment with both did not cause any additive effect on migration (E). In the 24 h assay the CB1 agonist ACEA, the CB2 agonist JWH-133 and the MAGL inhibitor JZL-184 (all at 0.5 μM) could all still significantly stimulate migration in the presence of the FGFR inhibitor PD173074 (1 μM) (F). In the presence of the CB receptor antagonists AM251 and JTE-907 (0.5 μM each), FGF-2 (2 ng/ml) still induced a significant migratory response in the 24 h assay. Graphs show mean ± SEM (n = 4); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Bar, 100 μm for (A–C).