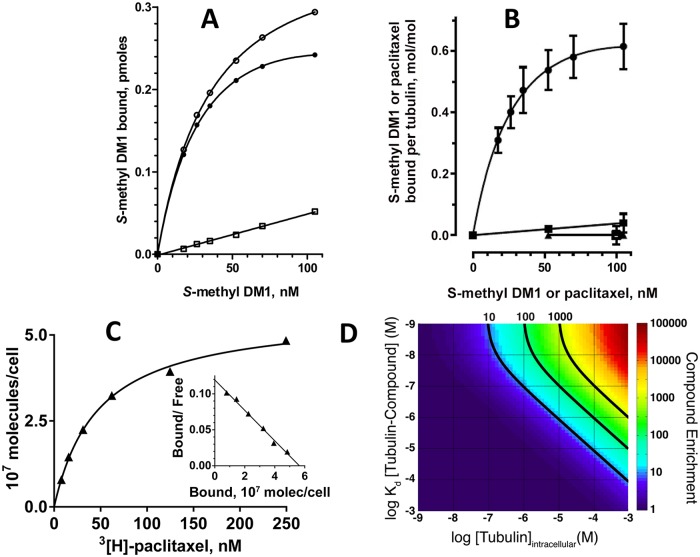
Fig 5. Accumulation of S-methyl DM1 in model systems.
A. Binding of 3[H]-S-methyl DM1 to tubulin-containing liposomes. In the representative experiment, liposomes formed in the presence of 97 μM tubulin were incubated with various concentrations of 3[H]-S-methyl DM1 at 37° C for 1.5 h (equilibrium was reached within 1 h) with (open squares) or without (open circles) an excess (6 μM) of non-labeled S-methyl DM1, then separated from non-bound 3[H]-S-methyl DM1 on a Sephadex G25 desalting column, and liposome-associated radioactivity was measured on a scintillation counter. The specific binding (filled circles) was calculated as the difference between the two values. B. Binding of 3[H]-S-methyl DM1 to tubulin-containing liposomes formed in the presence of a high (97 μM; circles) or a low (7 μM, squares) concentration of tubulin, or to tubulin in solution (triangles). The experimental conditions are similar to those in A. Also shown is specific binding of 3[H]-paclitaxel to to liposomes formed in the presence of 97 μM tubulin (open square). Each point (the mean ± standard error) is the result of two independent experiments. C. Specific binding of 3[H]-paclitaxel to MCF7 cells and the Scatchard plot, a representative experiment. D. Computation of accumulation of a tubulin-binding compound inside a cell containing tubulin (see text).