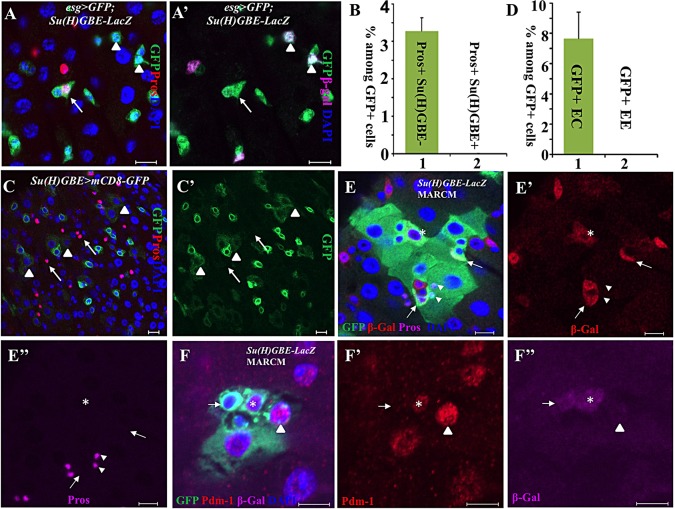
Fig. 1.
Su(H)GBE+ EBs are not EE progenitors. (A,A′) Esg+ (green) Pros+ (red) cells (arrows) do not express the EB marker Su(H)GBE-lacZ (arrowheads, purple in A′). (B) The quantification of Esg+ Pros+ Su(H)GBE− and Esg+ Pros+ Su(H)GBE+ cells among all Esg+ cells. Data are represented as mean±s.e.m. (C,C′) Some of the ECs (arrowheads) inherited weak GFP from Su(H)GBE+ EBs; none of the EEs (arrow) inherited GFP from Su(H)GBE+ EBs, suggesting that ECs, but not EEs, are developed from Su(H)GBE+ EBs. (D) The quantification of GFP+ ECs and EEs among all GFP+ cells in Su(H)GBE>GFP posterior midguts. Data are represented as mean±s.e.m. (E-E″) Wild-type MARCM clones with Su(H)GBE-lacZ. Some polyploid ECs (asterisks) express β-Gal inherited from Su(H)GBE-lacZ+ EBs (arrows). However, none of the EEs (arrowhead) expresses β-Gal, suggesting that ECs, but not EEs, are developed from Su(H)GBE+ EBs. (F-F″) Wild-type MARCM clones with Su(H)GBE-lacZ. The arrows indicate a β-Gal+ Pdm-1− EB. The asterisks indicate a β-Gal+ Pdm-1+ EC. The arrowheads indicate a β-Gal− Pdm-1+ EC. Scale bars: 10 μm.