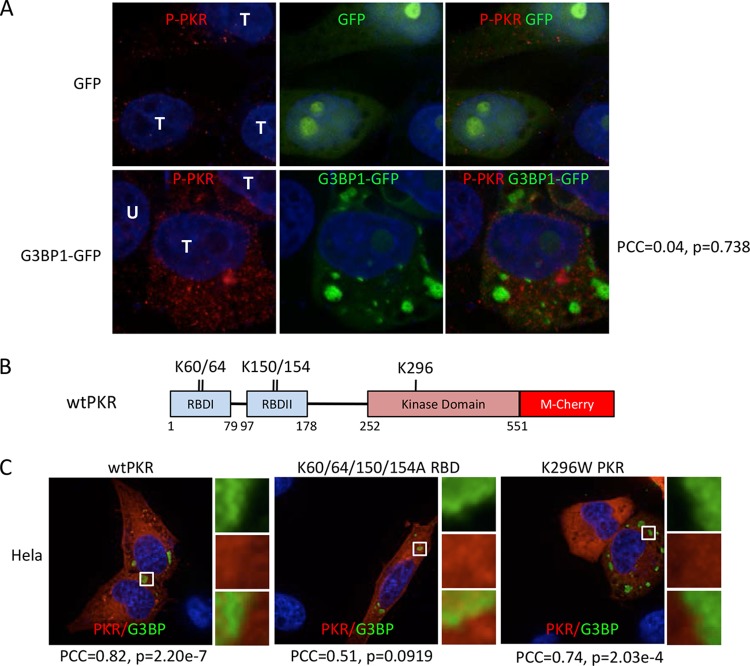
FIG 7.
Determinants of PKR recruitment to SGs. (A) Immunofluorescence microscopy with PKR phospho-T446-specific antibody. Cells were transfected with GFP or G3BP1-GFP, as indicated, and GFP localization was detected directly by fluorescence. T, transfected cells; U, untransfected cell. Pearson's correlation coefficient (PCC) for colocalization of P-PKR (red) with G3BP1-GFP (green), along with the relevant P value, are indicated on the right. (B) Domain map of human PKR with mutated amino acids indicated. RBD, RNA-binding domain. K60/64 and K150/154 are residues implicated in RNA binding; K296 is a key residue within the catalytic site of PKR. (C) G3BP1 expressed from pcDNA 3.1 HisC-G3BP1 (green) and hPKR-mCherry (red) were coexpressed in HeLa cells to investigate colocalization. Colocalization of the wild type, a K60/64/150/154A mutant deficient in RNA binding, and the K296W catalytically inactive PKR mutant was examined, as indicated. G3BP1 transgene expression was detected with anti-T7 antibodies. The PCC and P value for colocalization of each PKR mutant with G3BP1 are indicated.