FIG 1.
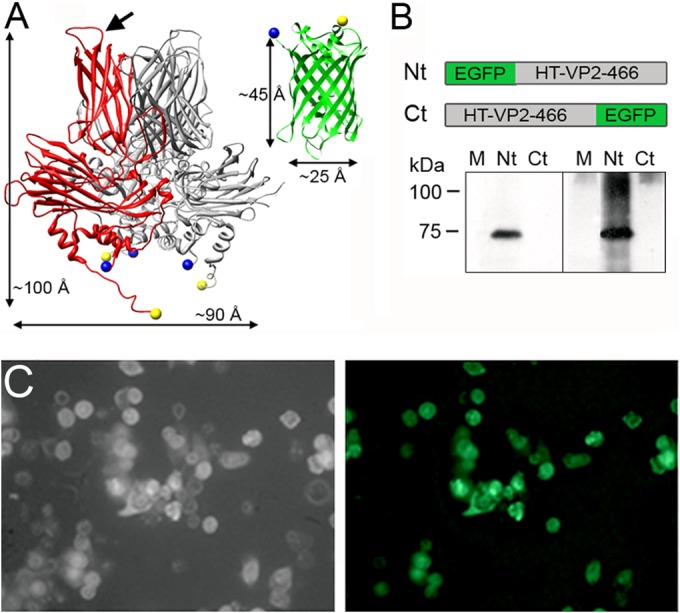
VP2 and EGFP structure and expression of EGFP-fused HT-VP2-466-based chimeric proteins. (A) (Left) VP2 trimer X-ray model (Protein Data Bank [PDB] accession number 2GSY) with a VP2 monomer (red). The VP2 chain (452 residues) lacks 7 N-terminal and 11 C-terminal residues; the first visible N-terminal amino acids and the last C-terminal amino acids are represented as blue and yellow circles, respectively (note that the N and C termini are close to each other). Arrow, PHI loop (located between the H and I β strands of domain P). (Right) EGFP X-ray model (green; PDB accession number 1GFL), with the N and C termini colored as described above. Dimensions are shown. (B) (Top) Scheme for HT-VP2-466-based chimeric proteins with EGFP fused to the N terminus (Nt; EGFP-HT-VP2-466) or to the C terminus (Ct; HT-VP2-466-EGFP). (Bottom) Extracts of H5 cells infected with rBV expressing both chimeras (Nt or Ct) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-GFP (left) or anti-VP2 (right) antibodies. Lanes M, molecular size markers (kDa). (C) Phase-contrast (left) and fluorescence (right) images of H5 cells expressing EGFP-HT-VP2-466. The fluorescent image was acquired with a Leica DMI6000B inverted microscope with the filter set for GFP.
