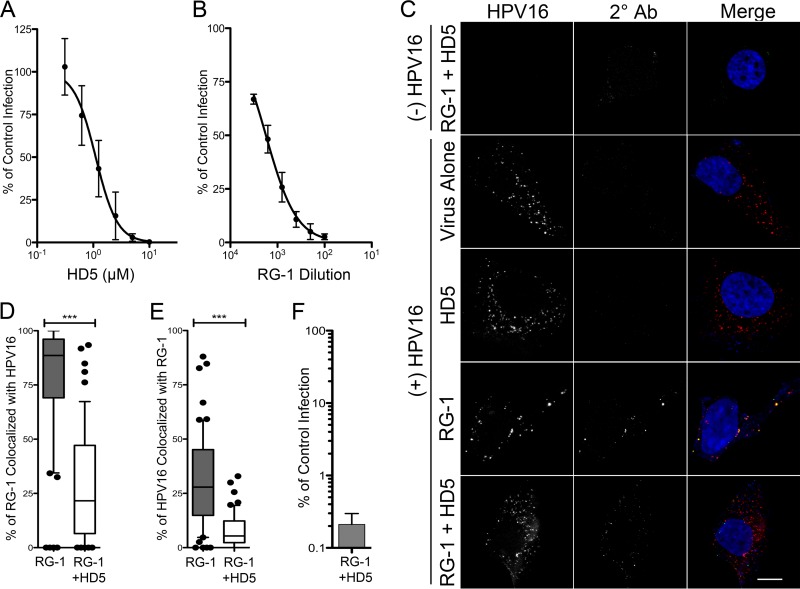
FIG 2.
(A) HD5 neutralizes AF555-HPV16 PsV in complete medium. HeLa cells were infected with AF555-HPV16 PsV incubated with increasing concentrations of HD5 in complete medium. Data are from three independent experiments normalized to control infection in the absence of inhibitor ± SD. IC50 = 1.1 μM, 95% CI = 0.93 to 1.32 μM. (B) RG-1 antibody neutralizes AF555-HPV16 PsV. HeLa cells were infected with AF555-HPV16 PsV incubated with increasing concentrations of RG-1 antibody in complete medium. Data are from three independent experiments normalized to control infection in the absence of inhibitor ± SD. IC50 = 1,759-fold dilution, 95% CI = 1,428- to 2,167-fold dilution. (C) The presence of HD5 prevents binding of the RG-1 antibody to HPV16 during cell entry. Images of HaCaT cells 12 h p.i. with [(+) HPV16] or without [(−) HPV16] AF555-HPV16 PsV in the presence of no inhibitor (virus alone), 5 μM HD5 (HD5), 5.4 μg/ml RG-1 antibody equivalent to a 200-fold dilution (RG-1), or 5 μM HD5 and 5.4 μg/ml RG-1 together (RG-1 + HD5). Individual panels depict maximum intensity z-projections of signal above the threshold for images in the z-stack that are coplanar with the nucleus for HPV16 (red) and RG-1 (2° Ab, green). In the merged images, the nucleus is blue. Scale bar is 10 μm. Manders coefficient values M1 (D) and M2 (E) are plotted as percentages of RG-1 colocalized with HPV16 and percentages of HPV16 colocalized with RG-1, respectively, for 50 to 60 cells for each condition. Whiskers are 5 to 95%, the horizontal line is the median, and outliers are depicted as individual points. ***, P < 0.0001. (F) HPV16 PsV treated with a combination of 5.4 μg/ml RG-1 and 5 μM HD5 is neutralized. Data are the means ± SD from 3 independent experiments normalized to infection in the absence of inhibitor.