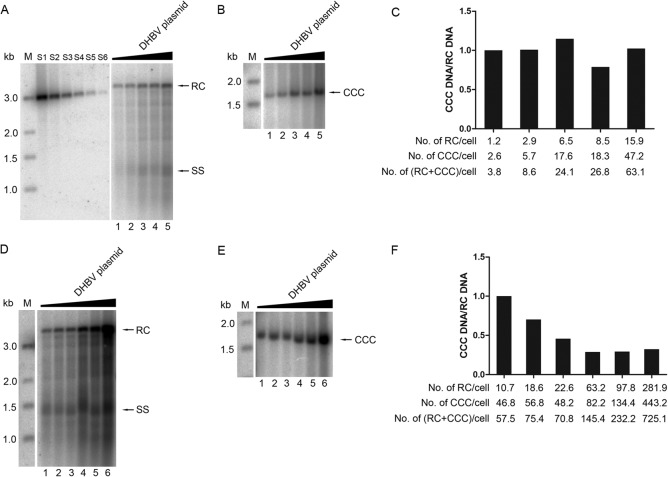
FIG 6.
Titration assay to estimate the efficiency of CCC DNA formation from increasing amounts of RC DNA. (A, B, D, E) Lanes 1 to 6, HEK293 cells in 60-mm dishes were transfected with pCMV-DHBV-Env– (0.03125, 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, and 0.5 μg for lanes 1 to 5 in panels A and B; 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 μg for lanes 1 to 6 in panels D and E). The GST expression plasmid was cotransfected to keep the total DNA amount per transfection constant (10 μg). RC DNA (A, D) and CCC DNA (B, E) were isolated and analyzed as described in the legends to Fig. 4 and 5, respectively. (C, F) The ratios of CCC DNA to RC DNA (CCC DNA/RC DNA) were estimated as described in the legend to Fig. 5 and normalized to that of lane 1, set to 1. Graph C is based on the results shown in panels A and B, and graph F is based on panels D and E. The average copy numbers of RC DNA, CCC DNA, and RC plus CCC DNA per cell are indicated at the bottom of the graphs. S1 to S6, 486, 162, 54, 18, 6, and 2 pg of the 3-kb DHBV DNA was loaded as quantification standards. M, DNA marker; RC, relaxed circular DNA; SS, full-length single-stranded DNA; CCC, covalently closed circular DNA.