FIG 2.
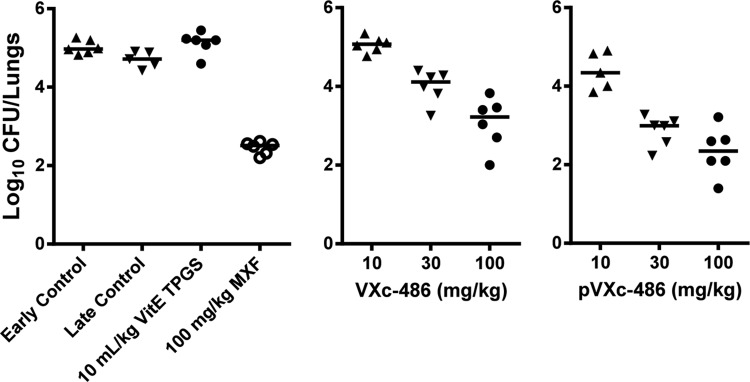
VXc-486 and pVXc-486 reduced the mycobacterial burden in a model of chronic tuberculosis infection in mice (Erdman isolate). The potencies of VXc-486 and pVXc-486, which target gyrase B, were compared with that of moxifloxacin (MXF), which targets gyrase A. VXc-486 and pVXc-486 were administered twice a day, while MXF was administered once a day, by oral gavage for 4 weeks at the doses indicated. Compared to the results for the early and late control groups, VXc-486 at 100 mg/kg, pVXc-486 at 30 and 100 mg/kg, and MXF at 100 mg/kg reduced the mycobacterial burdens by statistically significant amounts (P < 0.05). Mycobacterial burdens were measured by CFU counts from lung homogenates of M. tuberculosis-infected mice at the end of 4 weeks of treatment. Horizontal bars show mean results.
