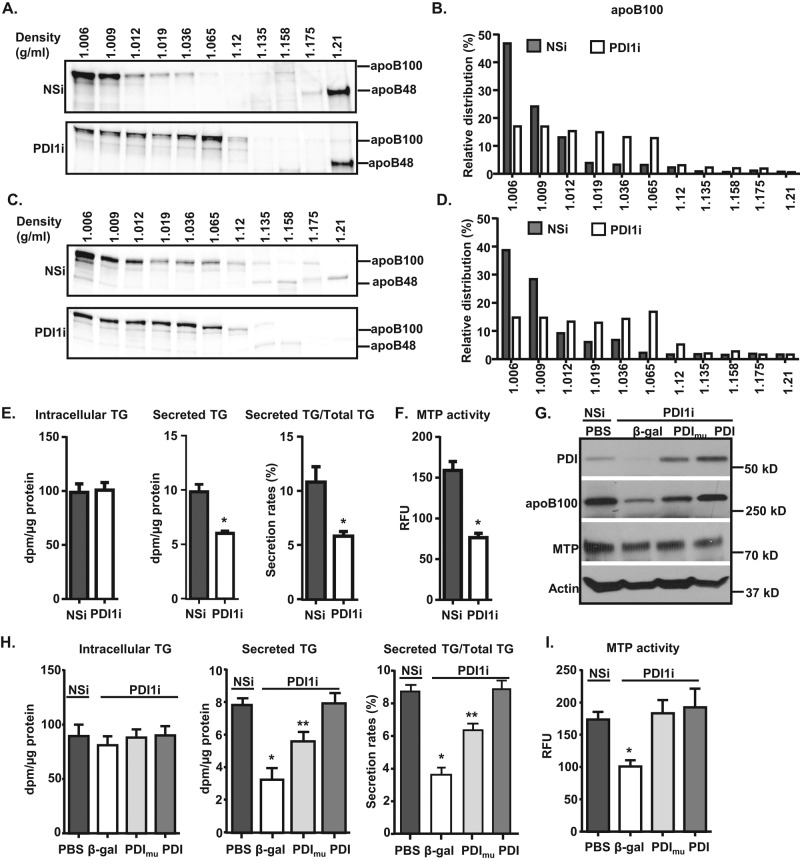
FIGURE 3:
Knockdown of Pdi1 decreases apoB100 lipidation in McA cells. (A–D) Pdi1 knockdown reduces apoB100 lipidation. McA cells were continuously labeled with [35S]Met/Cys containing BSA (A) or 400 μM OA (C) for 4 h. The medium was collected for determination of buoyant density of secreted apoB-containing lipoproteins from control (NSi) and Pdi1 knockdown (PDI1i) McA cells by DGUC, followed by immunoprecipitation for apoB100. The amount of apoB100 in each fraction was quantified by ImageJ. Relative distributions were calculated according to the percentage of apoB100 in each fraction relative to its total intensity across the gel (B, D). (E, F) Efficient TG secretion requires catalytically active PDI1. TG secretion (E) and MTP activity (F) were decreased in Pdi1-knockdown McA cells. TG synthesis and secretion (E) and MTP activity (F) were measured in control and Pdi1-knockdown McA cells. *p < 0.01 vs. NSi. (G–I) Overexpression of human wild-type PDI1 but not catalytically inactive PDI1 rescues decreased TG secretion in Pdi1-knockdown McA cells. (G) Wild-type and mutant PDI1 are expressed at equal levels in Pdi1-knockdown McA cells. β-Galactosidase (β-gal), human wild-type PDI1 (PDI), and catalytically inactive PDI1 (PDImu) were expressed using adenoviruses, and their expression levels were measured by Western blotting analysis. TG synthesis and secretion (H) and MTP activity (I) were measured in control cells or Pdi1-knockdown cells with overexpression of β-gal, PDI, or PDImu McA cells. PBS denotes no adenovirus infection. *p < 0.01 vs. PBS, PDI1, or PDI1mu; **p < 0.01 vs. PBS or PDI1.