FIGURE 1:
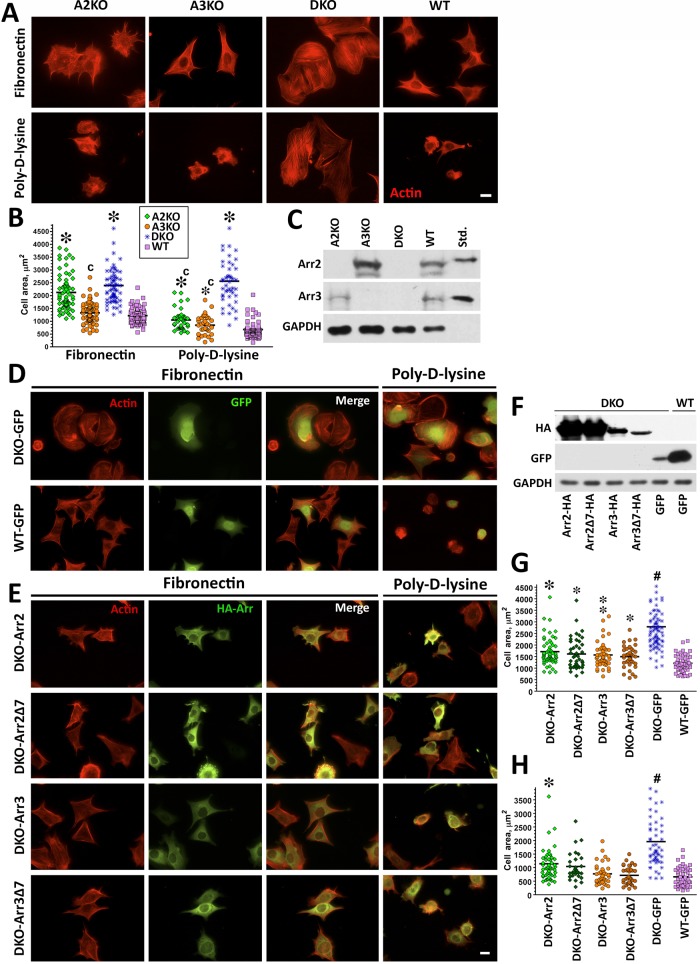
Knockout of both nonvisual arrestins dramatically alters cytoskeleton. (A) Cells lacking arrestin-2 (A2KO), arrestin-3 (A3KO), or both (DKO) and WT cells were stained with rhodamine–phalloidin after spreading for 2 h on FN or PDL. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) The size of 50 cells in each of the three experiments was quantified at each time point on FN or PDL. The cell size data were analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis analysis of variance, followed by posthoc pairwise comparison by Mann–Whitney test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.001 compared with WT, cp < 0.001 compared with DKO. (C) Expression of arrestins in DKO and WT cells was detected by Western blot. Purified bovine arrestin-2 and arrestin-3 (0.2 ng/lane) were run for comparison. (D, E) DKO cells were retrovirally infected with Ha-tagged arrestin-2 (Arr2), arrestin-2-Δ7 (Arr2Δ7), arrestin-3 (Arr3), arrestin-3-Δ7 (Arr3Δ7), or GFP as a control (DKO and WT). Cells were plated on FN and PDL. Arrestin-expressing cells were stained for actin and HA (E), and control cells were stained for actin and GFP (D). Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Western blots showing the expression of HA-arrestins and GFP. GAPDH is used as a loading control. (G) Cell size was measured on FN and analyzed as described for B. #p < 0.001 DKO from all other conditions, *p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 to WT. Data are from 37–82 cells/condition from three or four experiments. (H) Cell size was measured on PDL from 29–54 cells in three experiments and analyzed as in B. #p < 0.001 for DKO from all other conditions, *p < 0.001 from WT.