FIGURE 3:
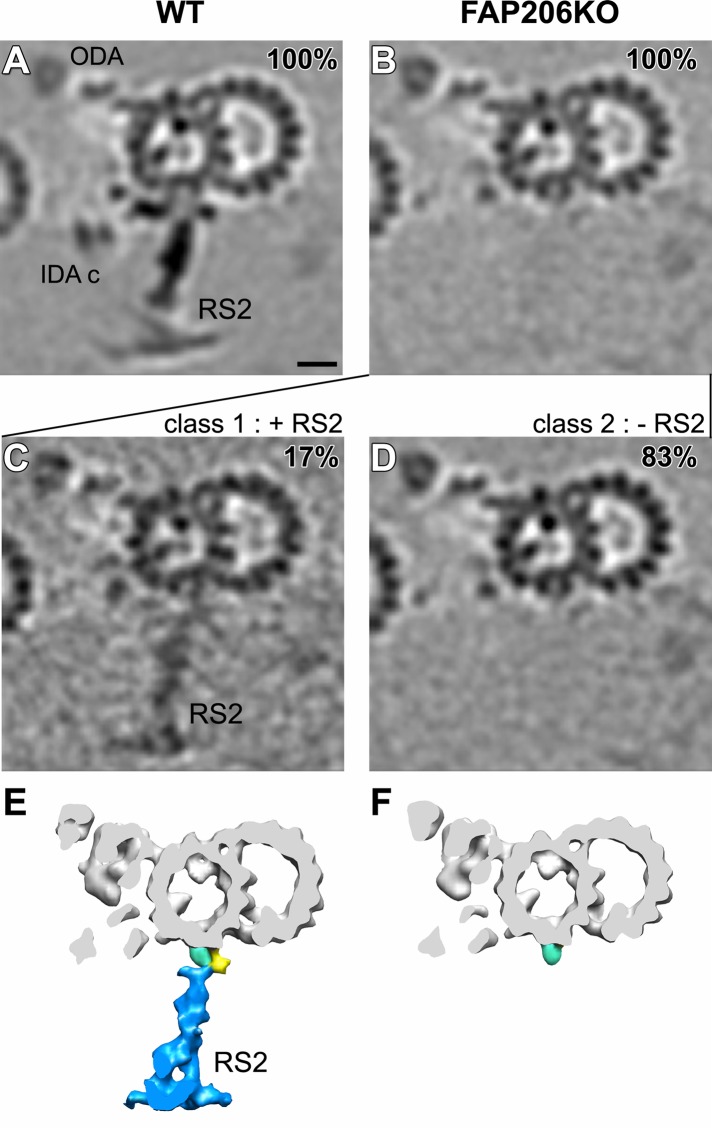
Classification analysis of RS2 reveals that in the absence of FAP206, RS2 can occasionally assemble but lacks the front prong. Cross-sectional tomographic slices (A–D) and isosurface renderings (E, F) of averaged 96-nm axonemal repeats show the presence and absence of RS2 in wild type (WT; A) and FAP206-KO (B–F), respectively. Subtomogram averages of all axonemal repeats (100%) indicate that the density of RS2 is dramatically reduced in FAP206-KO (B) as compared with WT (A). Classification of RS2 resulted in two distinct class averages for FAP206-KO: a large set (83%) of axonemal repeats from FAP206-KO lack RS2 (–RS2), and only the side prong (light blue) remains (D and F). However, in a small subset (17%) of FAP206-KO repeats, RS2 is present (+RS2) yet lacks the front prong density of the RS2 base (C and E); the back prong density also appears slightly reduced. All axonemal repeats from WT showed normal RS2 (A). Scale bar, 10 nm.