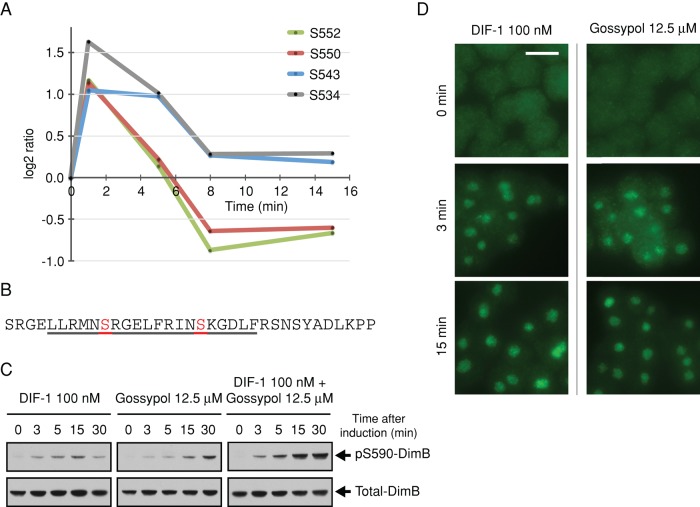
FIGURE 3:
DIF-1–regulated phosphorylation sites on CanA, the catalytic subunit of calcineurin, and its role in the regulation of DimB phosphorylation. (A) Temporal profile for DIF-1–induced phosphorylation changes in class I sites on CanA (DDB0185021). Phosphorylation fold changes are expressed as log2 ratios relative to pretreatment; a log2 ratio of 1 is a twofold increase in phosphorylation, whereas a log2 ratio of −1 represents a twofold decrease in phosphorylation, that is, dephosphorylation. (B) Amino acid sequence 525–559 of CanA. Underlined 529–548 is a putative CaM-binding domain (Catalano and O'Day, 2008). Highlighted and labeled residues are those identified as class I DIF-1 regulated. (C) DimB S590 phosphorylation in response to DIF-1 and gossypol treatment. Ax2 cells starved for 4 h were treated with DIF-1 and/or gossypol and samples collected at the times indicated and then immunoblotted using anti–pS590 DimB and anti–total DimB antibody. (D) Nuclear translocation of DimB in response to DIF-1 and gossypol. Cells developed and treated as in C. Nuclear accumulation of DimB was assayed immunohistochemically at the stated times using anti–total DimB. Ethanol and dimethyl sulfoxide controls (DIF-1 and gossypol, respectively) both showed no nuclear accumulation. Scale bar, 10 μm.