Figure 2.
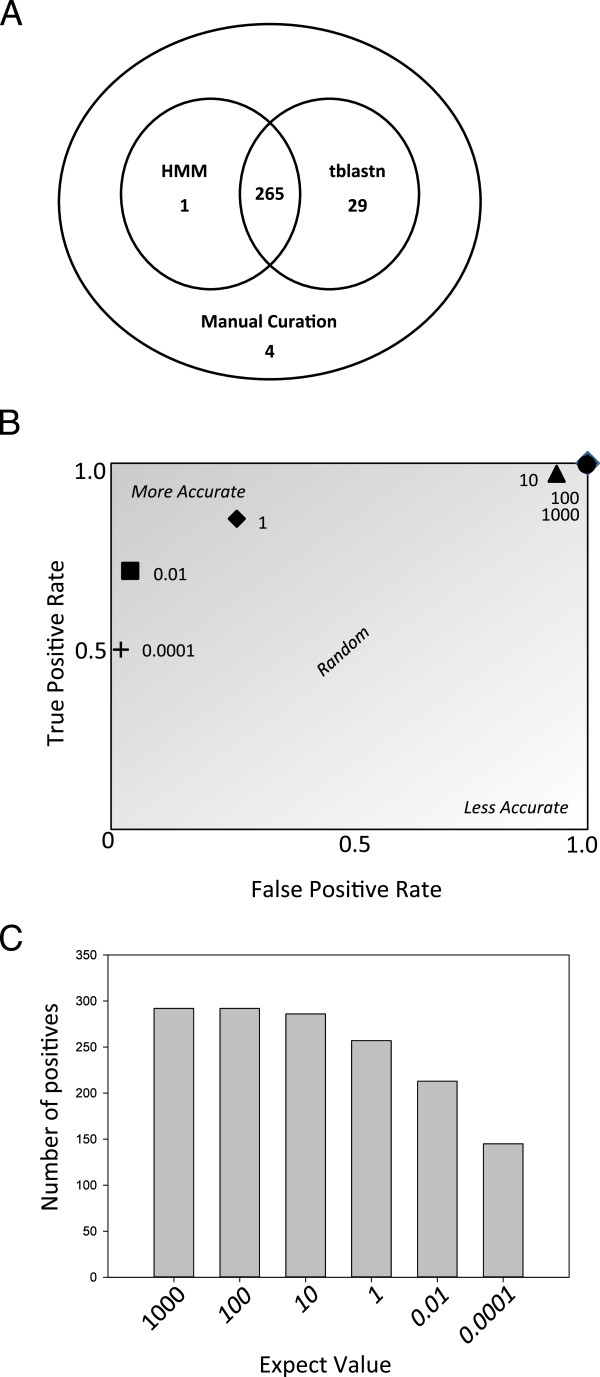
Evaluating methods for accurately identifying CydX homologues in 1121 species of bacteria. (A) Venn diagram of the number of CydX homologues identified by an HMM-based method (“HMM”), a tblastn screen of the NCBI microbial database using the CydX protein sequence as the query and an expect value of 1000 (“tblastn”), or by manual curation (“Missed”). (B) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) plot of a tblastn screen of the microbial database using the CydX protein sequence as the query with different E-value cutoffs. (C) Graph of the number of CydX homologues identified in a tblastn screen of the microbial database using the CydX protein sequence as the query with different expect values. All tblastn searches were conducted using the NCBI BLAST Microbial Genomes site [45].
