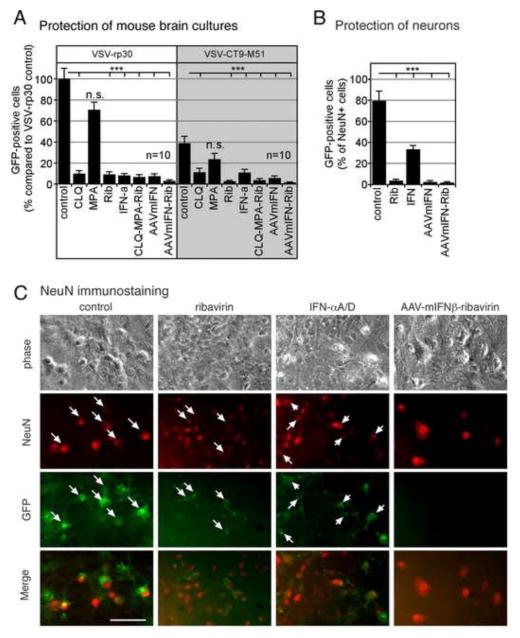
Figure 7. Effect of antiviral compounds and AAV-mIFN-β on infection of neuronal cultures.
(A) Mouse brain neuron cultures were pretreated for 6 hrs with either chloroquine (CLQ; 30 μM), MPA (300 μM), ribavirin (Rib; 300 μM), or IFN (100 IU/ml) and combinations thereof (CLQ-MPA-Rib). Cultures pretreated with AAV-mIFN-β were incubated for 10 days with a vector concentration of 5,000 genomes per cell. Cultures were infected with an MOI of 1 of VSV-rp30 or VSV-CT9-M51, respectively. At 36 hpi, infected cells were counted via fluorescence microscopy. Bars indicate analysis of ten microscopic fields, error bars expressed as SEM. (B) Neuronal marker NeuN was used to identify and quantify infection rates in neurons. The percentage of mouse neurons (NeuN+ cells) in murine brain cultures infected with VSV was determined 20hpi for unprotected cells, and for cells protected by IFN-αA/D (100 IU/ml), ribavirin (Rib; 300 μM), AAV-mIFN-β (5,000 genomes per cell), or AAV-mIFN-β + ribavirin. Error Bars, SEM. (C) Image panel of representative micrographs showing corresponding phase contrast, NeuN immunostaining, and GFP images. Merged images show co-localization of VSV infection on neurons (arrows) in control conditions (no pretreatment) and at much reduced rates in the treated cultures. *** indicates p<0.001 significance; n.s. = not significant (n=10; ANOVA with Bonferroni Post-Hoc Analysis). Scale bar 50 μm.