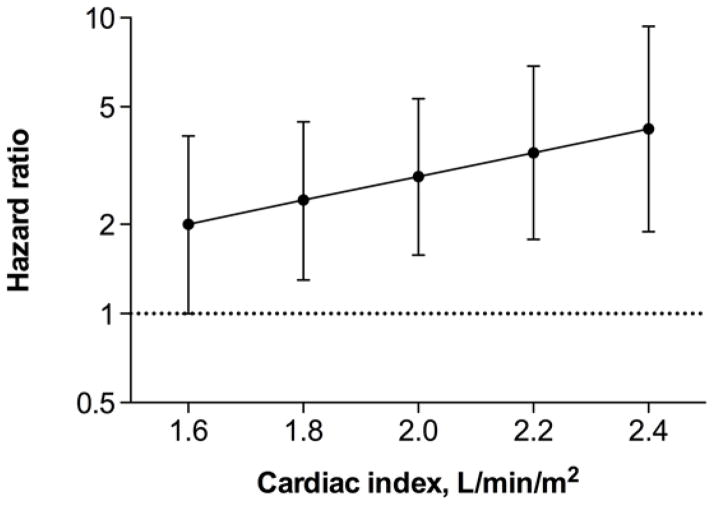
Figure 1.
In-hospital inotrope use and risk for death, ventricular assist device implantation, or heart transplantation by 180 days according to baseline cardiac index (N=196). The hazard ratio represents the effect of in-hospital inotrope use compared with no inotrope use as reference. There was a trend towards higher risk for major clinical events with use of inotropes with increasing cardiac index. The interaction term, however, was not statistically significant (P=0.092) in a model adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, left ventricular ejection fraction, admission systolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, sodium, and hemoglobin.