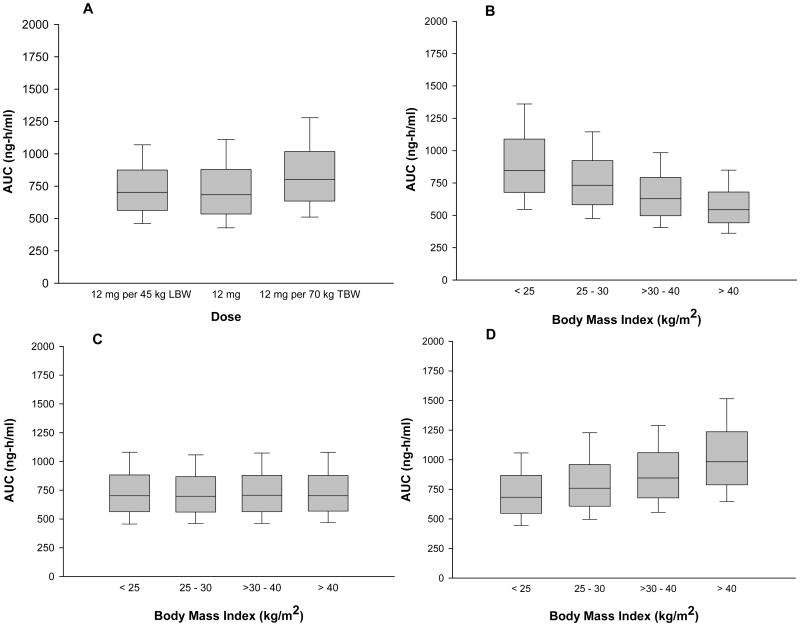
Figure 3.
Graphical evaluation of the effects of dosage regimen and body size on betamethasone exposure, as represented by the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC). AUCs were determined by simulating 1000 replicates of the final population model for each of the following doses: standard 12 mg, 12 mg per 45 kg LBW (LBW-adjusted dose) or 12 mg per 70 kg TBW (TBW-adjusted dose). (A) Box plot of simulated betamethasone AUCs for each of the 3 doses. (B) Box plot of simulated betamethasone AUCs following a 12 mg dose (not adjusted) grouped by the patients' body mass indices: < 25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, > 30-40 kg/m2 or > 40 kg/m2. (C) Box plot of simulated betamethasone AUCs following a 12 mg per 45 kg LBW dose (adjusted by LBW) grouped by body mass index: < 25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, > 30-40 kg/m2 or > 40 kg/m2. (D) Box plot of simulated betamethasone AUCs following a 12 mg per 70 kg TBW dose (adjusted by TWB) grouped by body mass index: < 25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, > 30-40 kg/m2 or > 40 kg/m2. The limits of the box represent the 25th to 75th percentile of the distribution, the solid line in the box is the median value and the whiskers represent the 10th and 90th percentiles of the distribution.