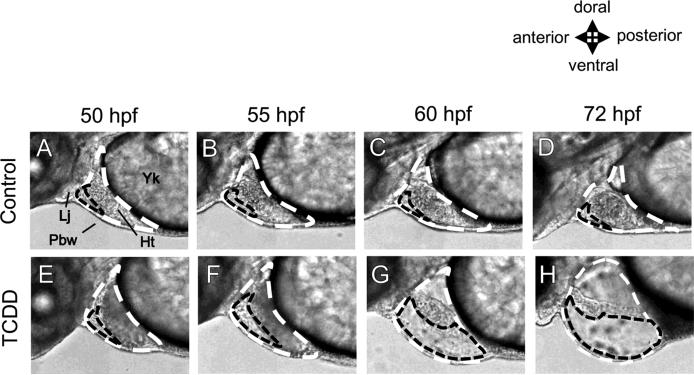
FIG. 1.
Precardiac cavity in comparison with pericardial cavity revealed by high-speed camera. Embryos were treated with either DMSO (Control) or 2 ppb TCDD, beginning at 24 hours post fertilization (hpf) until observation. All images are lateral views of developing zebrafish (50-72 hpf) with a focus on pericardial region. The pericardial cavity (white dashed line) around heart (Ht) is surrounded by the pectoral body wall (Pbw), lower jaw (Lj) and yolk (Yk) as indicated in panel A. Otherwise, a smaller cavity surrounded by the front edge of the heart, pectoral body wall and lower jaw can be recognized (black dashed line). For evaluation of pericardial edema (former method), pericardial cavity (white dashed line) was circled on photoshop image and the area was determined in pixels. For precardiac edema (new method), small cavity between heart and body wall in maximal diastole (black dashed line) was quantified in pixels. Upper panels (A-D): control, lower panels (E-H): 2 ppb TCDD.