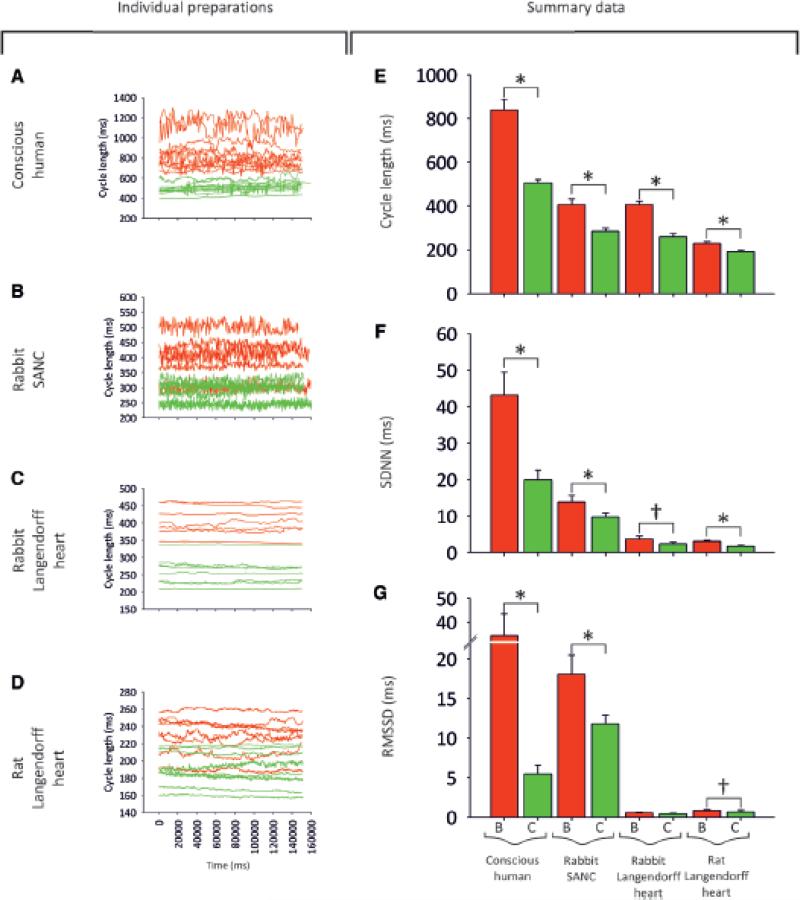
Fig. 2. Effect of β-agonists on HRV in different cardiac preparations.
A-D, tachograms demonstrating the effect of β-agonists on HRV. A, before and after dobutamine in conscious humans. B, data before and after 100 nM isoprenaline in rabbit SANC. C, data before and after 100 nM isoprenaline in Langendorff-perfused rabbit hearts. D, data before and after 100 nM isoprenaline in Langendorff-perfused rat hearts. Baseline data = red, data in presence of β-adrenergic agonist = green. E-G, summary of the effect of β-adrenergic agonists on HRV. Mean (+SEM) CL (E), SDNN (F), and RMSSD (G) under baseline conditions (= ‘B’; red bars) and with β-adrenergic agonist (= ‘C’; green bars) for the different preparations. Asterisk and bar = statistically different (P<0·05; 1-way ANOVA). Sword and bar = P=0·1>P>0·05.