Figure 3. Results of In Vitro Functional Assays of Common TBX6 Variants and the Mechanistic Model of TBX6-Associated Congenital Scoliosis.
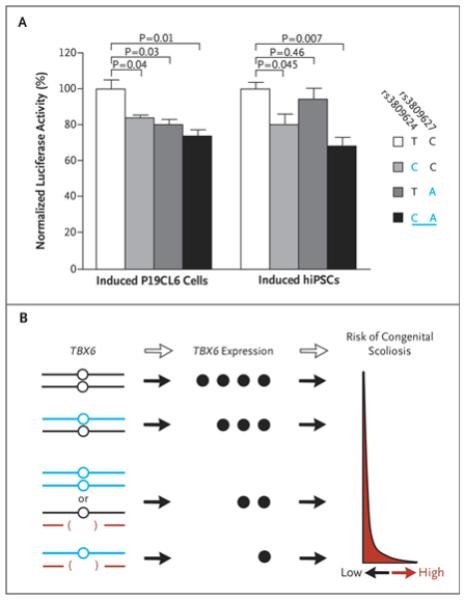
Panel A shows the results of luciferase reporter assays. Two cell types (P19CL6 cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells [hiPSCs]) with high levels of expression of TBX6 during induced differentiation were used. The nonreference alleles of rs3809624 and rs3809627 are shown in blue, and the risk haplotype is underlined. At least three independent experiments of normalized luciferase activity were quantified, with the graph showing mean values and their standard errors (I bars). Panel B shows a simplified genetic model of TBX6-associated congenital scoliosis. TBX6 expression is critical for normal vertebral formation (the reference allele of TBX6 is indicated by a black line). Heterozygous hypomorphic variants (shown in blue) cause only a moderate reduction in TBX6 expression. Even homozygous hypomorphic variants do not reduce TBX6 expression dramatically. Heterozygous TBX6 null mutations (indicated by red brackets) may reduce gene expression by one half. Independently, these mutations hardly reach the gene-dosage threshold for congenital scoliosis. In combination, however, a null allele and a hypomorphic allele of TBX6 cause further reductions in gene expression that may confer a high risk of congenital scoliosis.
