Figure 6.
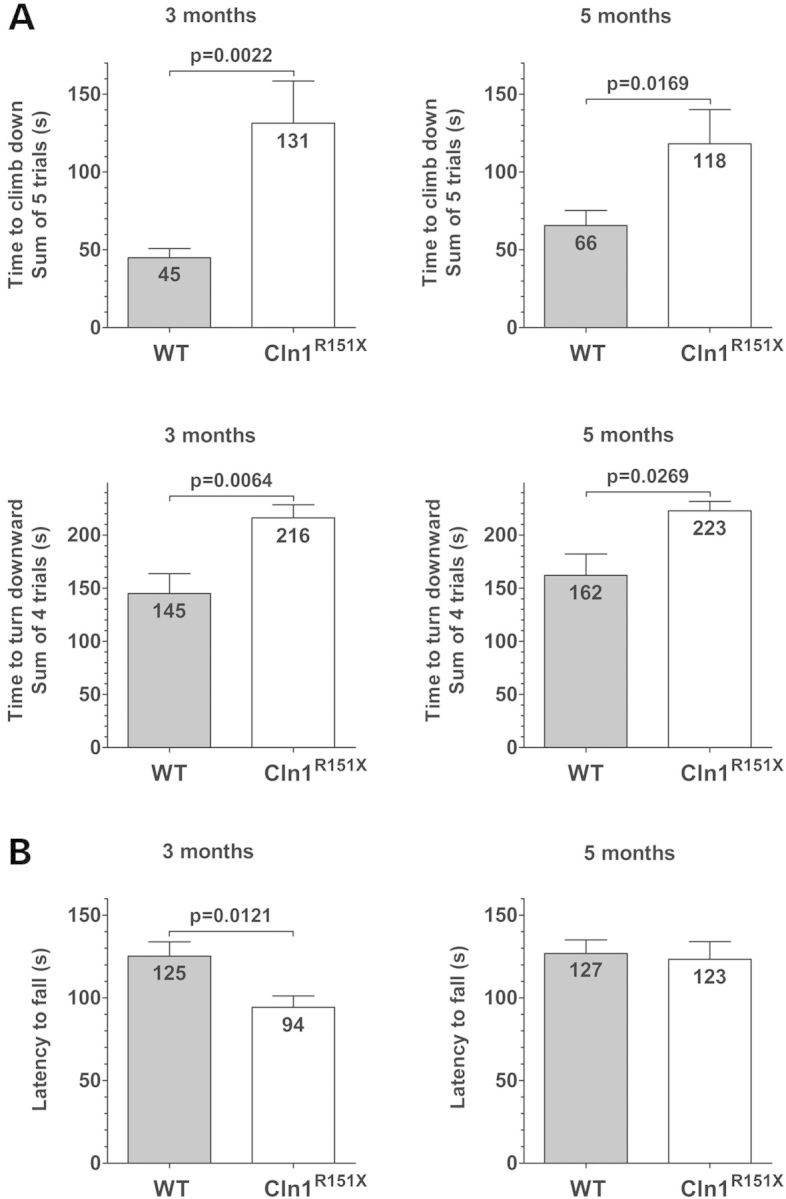
Cln1R151X mice have motor deficits as measured by the vertical pole test and rotarod test. The motor skills of WT and Cln1R151X male mice were examined at 3 and 5 months of age. (A) In the modified vertical pole test, Cln1R151X mice climbed down on the pole drastically slower (upper 2 graphs), and turned downward on the pole significantly slower (lower 2 graphs) than WT mice. Columns and bars represent mean ± SEM. The same WT and Cln1R151X mice were tested at 3 and 5 months of age (14 WT and 12 Cln1R151X mice). Statistical significance was determined by the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. (B) In an accelerating rotarod test (0.2 rpm/s starting from 0 rpm), 3-month-old Cln1R151X mice fell from the rotating rod 31 s sooner than WT mice (left graph). At the age of 5 months, the rotarod performance of Cln1R151X and WT mice was similar (right graph). Columns and bars represent mean ± SEM. The same WT and Cln1R151X mice were tested at 3 and 5 months of age (14 WT and 12 Cln1R151X mice). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test.
