Fig. 5.
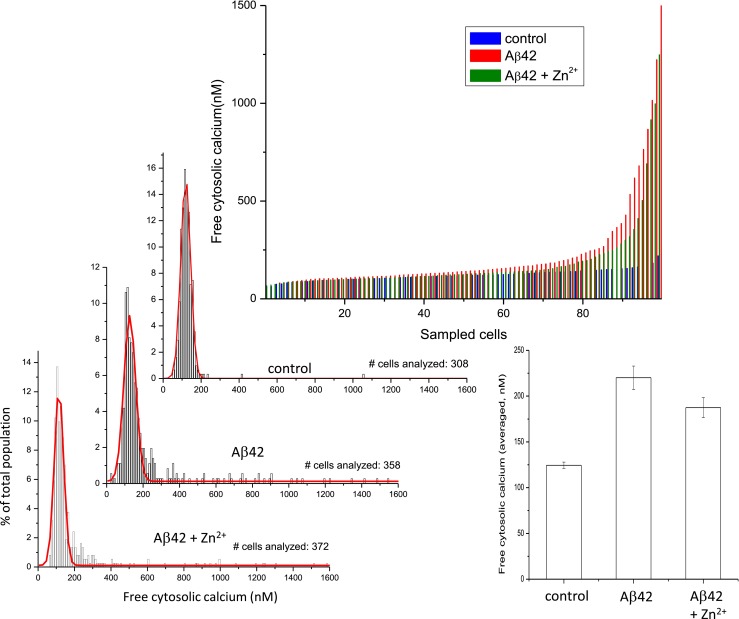
The Aβ channel blocker Zn2+ prevents the slow increase in intracellular calcium concentration in neurons. Single-cell measurement of intracellular [Ca2+] levels in the cells exposed to Aβ42 alone (red lines) and Aβ42 plus Zn2+ (blue lines) after 3 days. Continuous exposure to Aβ42 creates a subpopulation of cells with cytosolic calcium levels higher than average. The channel blocker Zn2+ markedly blunted the increase in intracellular calcium induced by Aβ in the subpopulation of Aβ42 more sensitive cells. Zn2+ also diminished the effect of calcium elevation from Aβ42. The bar plot corresponding to the averaged free cytosolic calcium of the whole cell population shows some protection by Zn2+ but does not reveal the highly effective protection by Zn2+ on the subpopulation of neurons that suffered the lowest calcium increases
