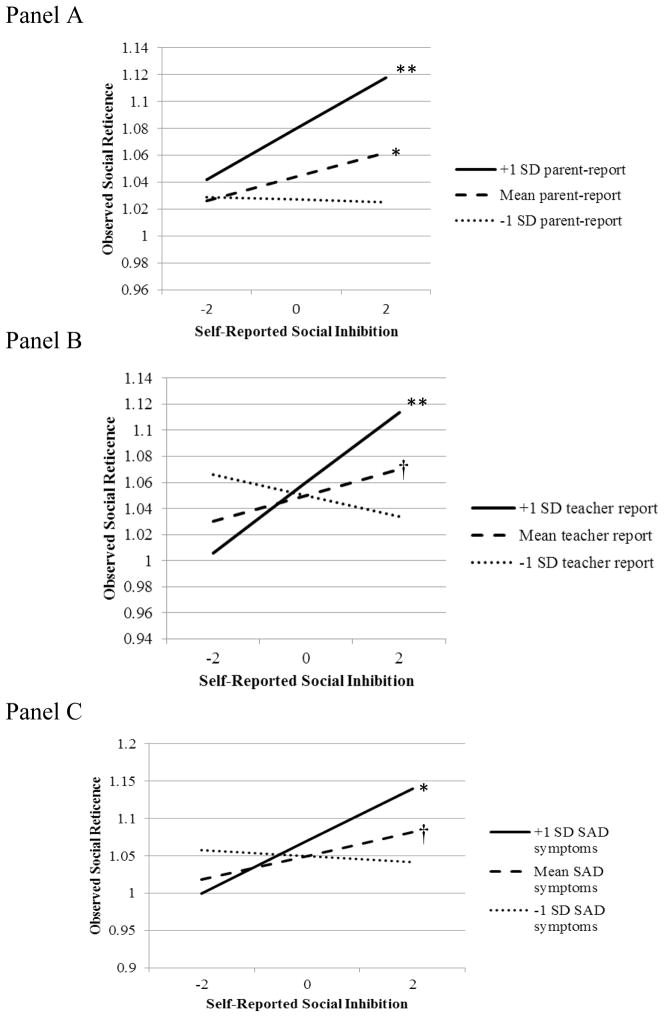
Figure 1.
Interactions between kindergarteners’ self-reported social inhibition and parent-report (Panel A), teacher-report (Panel B), and Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) symptoms obtained from a parent interview (Panel C). Quadratic effects of child report and the moderator were included in all models. All three interactions were significant. Probing revealed that children’s self-reported social inhibition related to observed social reticence at high levels of these moderators.
†p < .10, *p < .05, **p < .01.