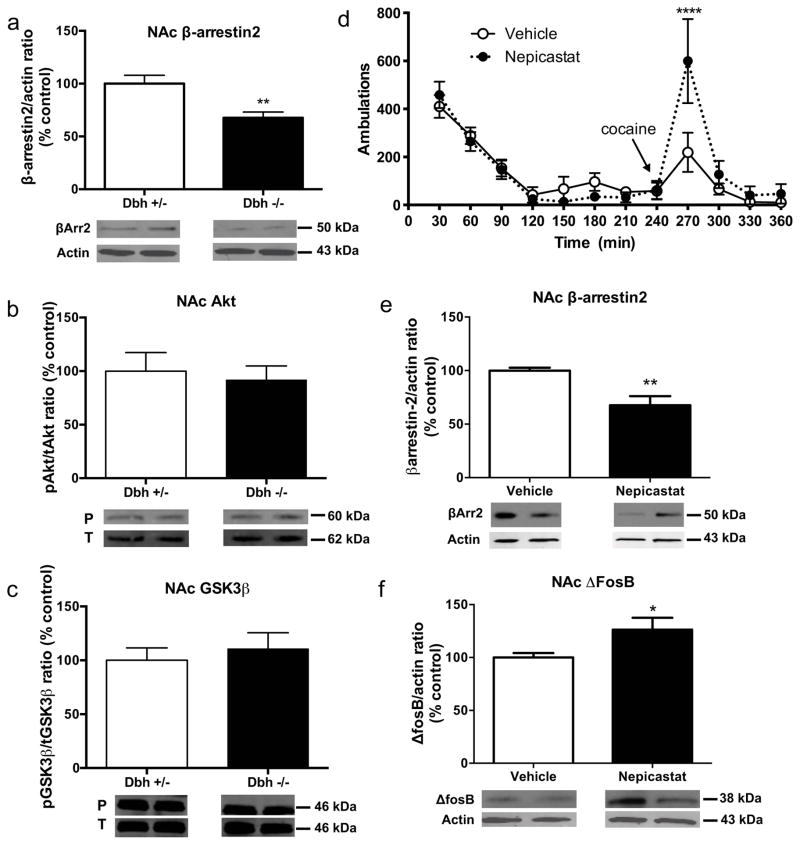
Figure 1. Behavioral and neurochemical phenotypes of mice with chronic DBH deficiency.
Western blot data (mean ± SEM above, representative blot below) for (a) βArr2:actin ratio, (b) protein kinase B (Akt; phospho:total ratio) and (c) glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β; phosphor:total ratio) in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of Dbh +/− and Dbh −/− mice (n = 8 per group). *p < 0.05 compared to Dbh +/− mice. (d) Cocaine-induced (10 mg/kg, i.p.) locomotion, (e) βArr2:actin ratio, and (f) ΔFosB:actin ratio in the NAc of Dbh +/− control mice treated chronically with the selective DBH inhibitor nepicastat. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 compared to vehicle.