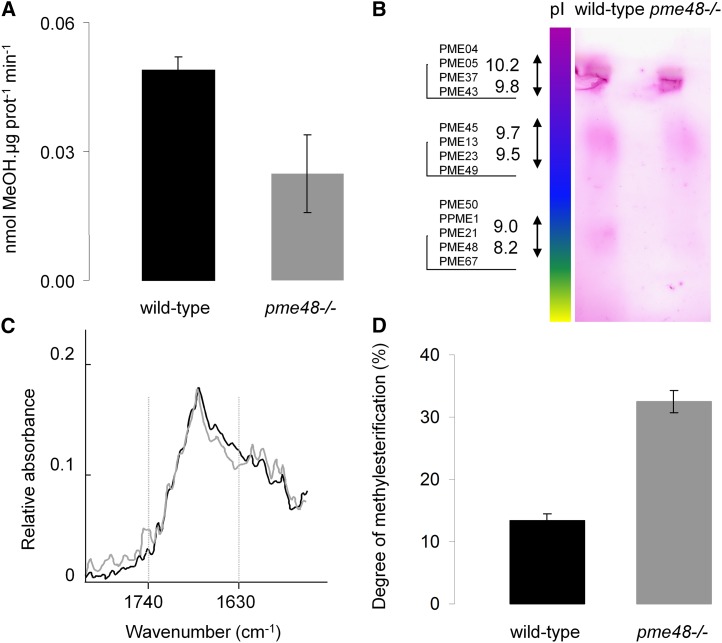
Figure 5.
Biochemical analyses of wild-type and pme48−/− dry pollen grains. A, Enzymatic assay of the total PME activity contained in wild-type (black bar) and pme48−/− dry (gray bar) pollen grains. MeOH, Methanol. B, Zymogram after IEF of PMEs contained in wild-type and pme48−/− dry pollen grains. A diffuse band corresponding to the pI (8.2) of PME48 is lacking in pme48−/− dry pollen grains. C and D, Determination of the DM of the HG in dry pollen grains by FT-IR spectroscopy. C, Representative FT-IR spectra of pectin-enriched fractions extracted from wild-type (black trace) and pme48−/− (gray trace) dry pollen grains. D, Quantification of the DM of HG in wild-type (black bar) and pme48−/− (gray bar) pollen grains. Data are means of three biological replicates ± sd.