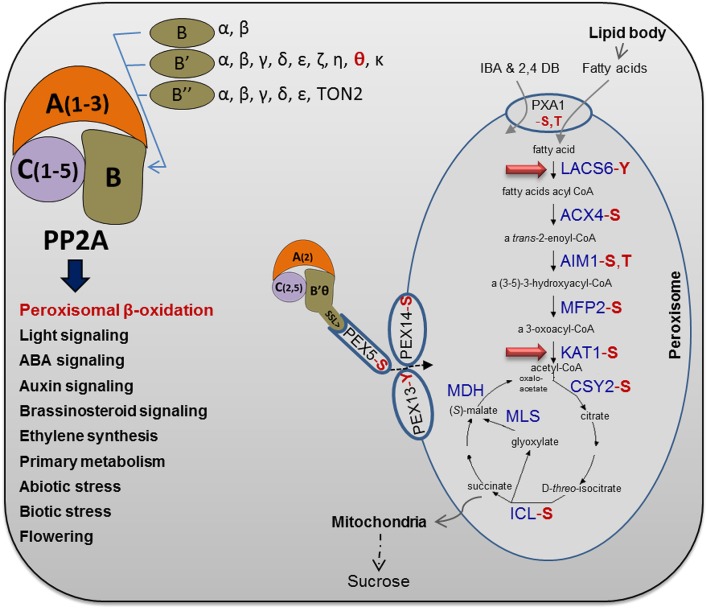
Figure 9.
Brief overview of Arabidopsis PP2A heterotrimer complexity and functions. The PP2A heterotrimer subunits are presented together with functions of PP2A in Arabidopsis (Farkas et al., 2007; Uhrig et al., 2013). Regulation of peroxisomal β-oxidation is a unique function of PP2A that was approved in this study. Several peroxisomal proteins, involved in fatty acid β-oxidation and the glyoxylate cycle, have been shown experimentally to be phosphorylated (Supplemental Table S1), as highlighted in red for the type of phosphorylated amino acid (S, Ser; T, Thr; and Y, Tyr). As highlighted by the red arrows, β-oxidation steps including LACS5 and KAT1 were found to be potential substrates for a peroxisomal PP2A heterotrimer based on the differences between phosphoproteomes of the b’θ mutant and the wild type (this work). For more details, see Table I. The protein abbreviations are as follows: ACX, acyl-CoA oxidase; AIM, enoyl-CoA hydratase; CSY, citrate synthase; ICL, isocitrate lyase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; MFP, multifunctional protein; and MLS, malate synthase. In glyoxysomes, the acetyl-CoA produced by fatty acid β-oxidation is used as a substrate for the glyoxylate cycle, where succinate is produced and transferred to mitochondria to be metabolized for energy production. Moreover, the peroxisomal ATP-binding cassette transporter (PXA1) and the PEX5, PEX13, and PEX14 were found to be phosphorylated (Supplemental Table S1). The pathway of fatty acid β-oxidation and glyoxylate cycle is modified from the online database (Karp et al., 2005).