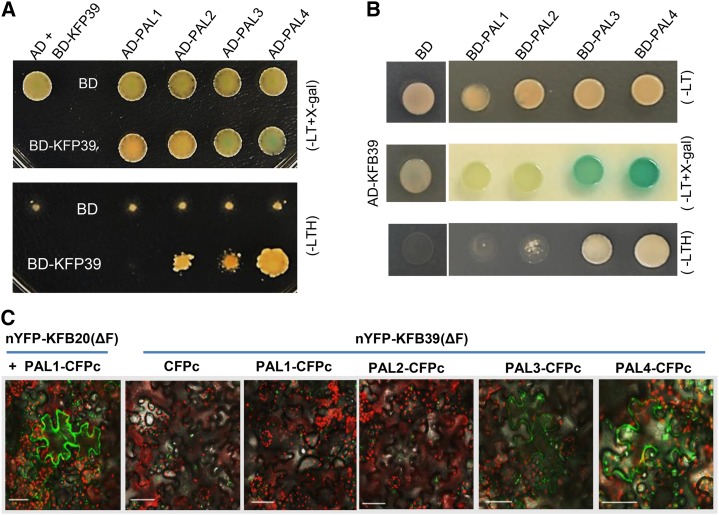
Figure 2.
Interaction of PAL isozymes with the KFB39 protein. A, Y2H assay between BD-KFB39 and AD-GADT7-PAL (PAL1–PAL4). Yeasts were grown on two-amino acid dropout (−Leu/Trp; −LT) synthetic defined (SD) medium supplemented with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (X-gal; top) or on three-amino acid dropout (−Leu/Trp/His; −LTH) selective medium (bottom). B, Domain-swapping validation of the interaction between KFB39 and PAL1 to PAL4 in Y2H assays. The assays were conducted between AD-KFB39 and BD-PAL (PAL1–PAL4). Yeasts were grown on SD (−Leu/Trp) medium in the absence (top) and presence (middle) of X-gal and on SD (−Leu/Trp/His) selective medium (bottom). C, BiFC assay for the interactions of PAL isozymes with KFB39 protein in transiently expressed tobacco leaves. PAL1 to PAL4 were fused with CFPc at their C termini, and the truncated KFB39(ΔF) was fused with nYFP at its N terminus. The truncated KFB39(ΔF) fusion construct was coinfiltrated with PAL-CFPc (or CFPc alone) in tobacco leaves. The pair of nYFP-KFB20(ΔF) with PAL1-CFPc served as a positive control. Bars = 50 μm.