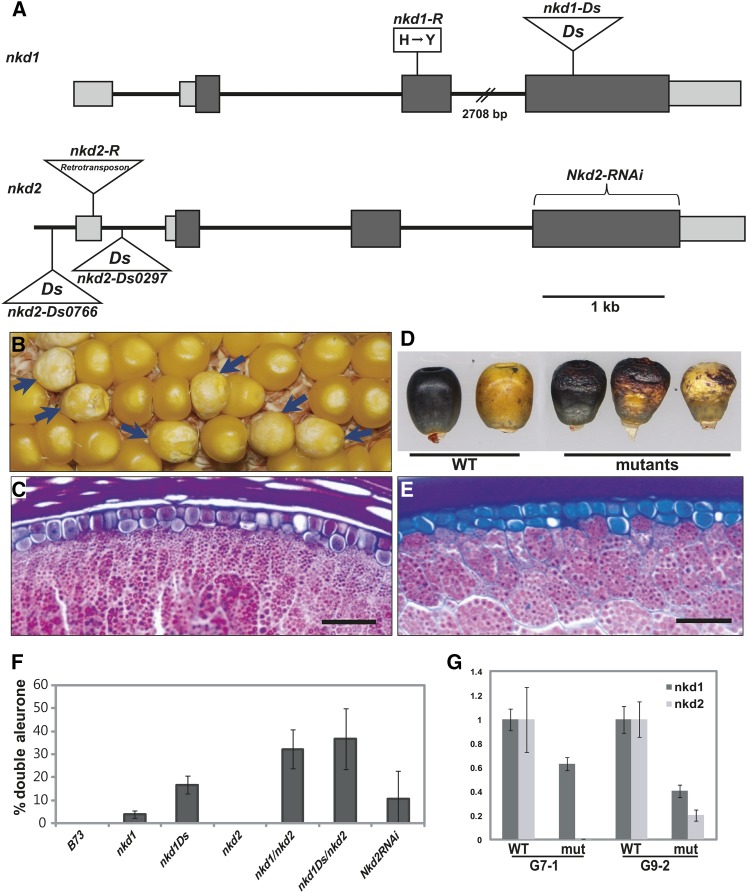
Figure 4.
Genetic confirmation of the nkd1 and nkd2 loci. A, nkd gene structures and alleles. The nkd1-R allele has an amino acid change (H→Y) at residue 102. The nkd1-Ds allele has a Ds insertion in the fourth exon. The nkd2-R allele contains a copia-like retrotransposon insertion in the first exon. The nkd2-Ds alleles have Ds insertions in the putative promoter region and the first intron. RNAi lines were generated using the fourth exon of nkd2. Boxes represent exons, and dark shading indicates a coding region. B, nkd1-Ds/+ self-pollinated ear showed 3:1 segregation for kernels with weak nkd phenotypes and rough-textured opaque endosperm, associated with nkd1-Ds homozygotes. Arrows indicate mutant kernels. C, Section of an nkd1-Ds homozygous kernel shows irregular double-layered aleurone. D, nkd2-RNAi line (G7-1) segregated kernels with wild-type (WT) and nkd phenotypes. Mutant kernels show wrinkled endosperm and sporadic disruption of anthocyanin pigmentation. E, nkd2-RNAi mutant kernel section shows irregular double-layered aleurone. F, Different nkd mutants show different levels of nkd phenotypes in terms of doubled aleurone. The degree of nkd phenotype strength was measured as the percentage of double-layered aleurone. Kernels were scored by counting 150 aleurone cells across the crown of the kernel and calculating the ratio of secondary aleurone cells as a percentage. nkd1-R sometimes showed multiple layers of aleurone. The nkd1-Ds allele has a stronger phenotype than nkd1-R. The phenotype became stronger when nkd2-R was added. G, nkd2-RNAi shows reduced transcript levels for both nkd1 and nkd2 in independent events, G7-1 and G9-2.