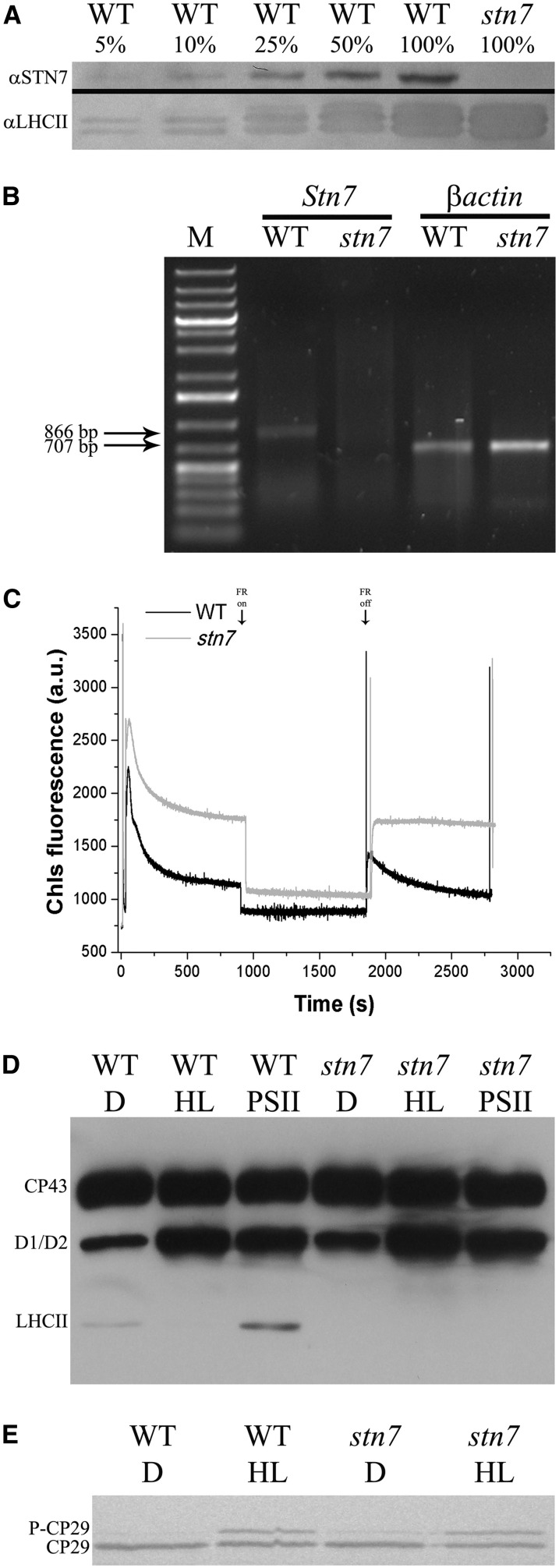
Figure 2.
Isolation and characterization of rice stn7 mutant. A, Immunoblot analysis using anti-STN7 antibody (αSTN7). Thylakoids have been isolated from wild-type (WT) and stn7 rice plants and then loaded on Tris-Tricine SDS-PAGE 10%. Wild-type 100% and stn7 100% correspond to 2 µg of Chl. An immunoblot analysis using anti-LHCII antibody αLHCII has been performed as an internal control. B, Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR measurement of gene-specific transcripts. Sequences of the oligonucleotides used are reported in “Materials and Methods.” The expected sizes of the PCR products are as follows: Stn7, 866 bp; and βactin, 707 bp. M indicates molecular mass marker (1-kb Plus Ladder, Thermo Scientific). C, Analysis of state transition in stn7 mutant. Chlorophyll fluorescence emission was measured upon treatment with blue light and blue light supplemented with far-red (FR) light, which induce transition to State 2 and State 1, respectively. a.u., Arbitrary unit. D, Analysis of thylakoid phosphoproteins using anti P-Thr (Cell Signaling) antibody. Rice wild-type and stn7 mutant leaves were either dark adapted (D) or treated with HL (1,500 µmol photons m–2 s–1, 30 min) or PSII-specific light (PSII; 100 µmol photons m–2 s–1, 1 h, orange filter), and then thylakoids have been collected (Suorsa et al., 2004). Tris-Gly SDS-PAGE 15% plus Urea 3M; 0.75 µg of Chl per lane. E, Evaluation of rice stn7 mutant capacity to phosphorylate CP29 upon HL induction (1,500 µmol photons m–2 s–1, 30 min). Wild-type and stn7 rice leaves were illuminated, and then thylakoids have been collected and loaded on SDS-PAGE. Immunoblot analysis as in Figure 1A. One microgram of Chl per lane.