FIGURE 2.
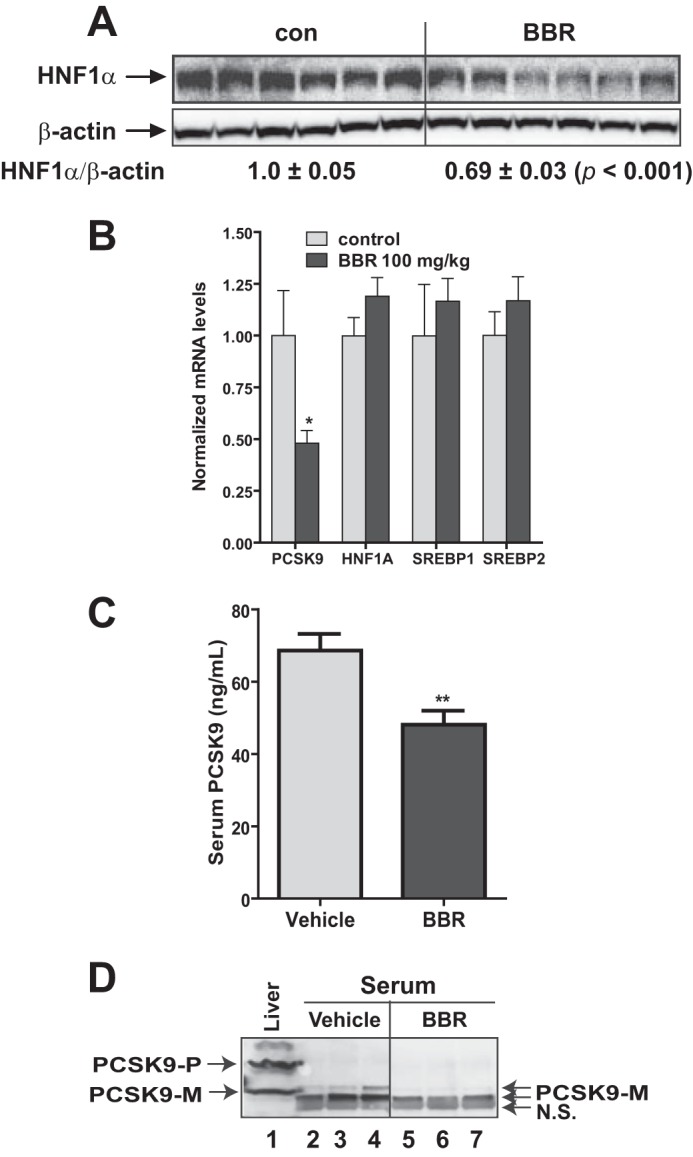
Reduction of serum PCSK9 and hepatic HNF1α protein in dyslipidemic hamsters by BBR treatment. Male hamsters were fed a high fructose diet for 3 weeks, which elevated serum TC and LDL-C (15). Hamsters on the high fructose diet were orally dosed with 100 mg/kg/day BBR (n = 9) or an equal volume of vehicle (10% 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin) as the control group (n = 9) for 7 days. A, 50 μg of homogenate proteins of six representative hamster liver samples from each group were resolved by SDS-PAGE. HNF1α and β-actin were detected by immunoblotting. The protein abundance of HNF1α was quantified with the Alpha View software with normalization by signals of β-actin. B, qPCR analysis of hamster liver mRNA levels of the indicated genes after BBR treatment. C, hamster serum PCSK9 levels after BBR treatment were determined using a mouse PCSK9 ELISA kit. D, three hamster serum samples of the same treatment group were pooled together. For each group, 20 μl of pooled serum of three pooled samples were used for conducting PCSK9 IP and Western blotting. Hamster liver homogenate protein was loaded in lane 1 as a positive control for anti-PCSK9 antibody Western blotting. The values are presented as mean ± S.E. (error bars). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 as compared with the vehicle group.
