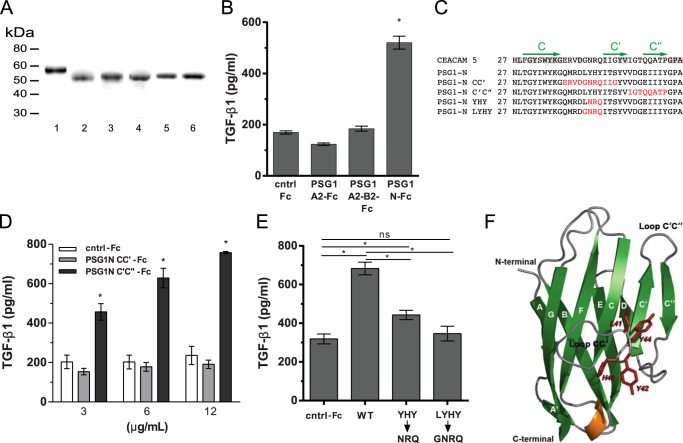
FIGURE 6.
Amino acids in the CC′ loop region of the N-terminal domain of PSG1 are essential for induction of TGF-β1 from RAW264.7 macrophages. A, recombinant proteins used for these studies were separated on a 4–20% NuPAGE gel and stained with GelCode Blue. Lane 1, PSG1-A2-B2-Fc; lane 2, PSG1-N-Fc; lane 3, PSG1-N-CC′-Fc; lane 4, PSG1-N-C′C″-Fc; lane 5, PSG1-N-YHY-Fc; lane 6, PSG1-N-LYHY-Fc. B, TGF-β1 secretion following incubation of RAW264.7 murine macrophages with 3 μg/ml control Fc protein (cntrl-Fc), PSG1-A2-Fc, and PSG1-N-Fc or 6 μg/ml PSG1-A2-B2-Fc to achieve concentrations equimolar to the single-domain proteins. C, sequence alignment of the CC′ and C′C″ loop regions of CEACAM5, PSG1, and PSG1 N-terminal domain mutants. Residues conserved in CEACAM5 and PSG1 are highlighted in gray. The C, C′, and C″ β-strands are indicated with green arrows above the corresponding sequence. Residues in the PSG1 N-terminal domain mutated to the residues corresponding to the same position in CEACAM5 are colored red. D, TGF-β1 secretion of RAW264.7 macrophages following incubation with increasing concentrations of PSG1-N-CC′-Fc, PSG1-N-C′C″-Fc, or control Fc protein. E, RAW264.7 macrophages were incubated with 12 μg/ml wild-type PSG1 N-terminal domain (WT), PSG1-N-Y42N/H43R/Y44Q mutant (YHY→NRQ), PSG1-N-L41G/Y42N/H43R/Y44Q mutant (LYHY→GNRQ), or control Fc protein. For B–E, TGF-β1 following acid activation was measured in the supernatants by ELISA as described under “Experimental Procedures.” *, p ≤ 0.05 by Student's t test; ns, not significant. F, ribbon representation of the structural model of the PSG1 N-terminal domain. β-Sheets are shown in green and labeled with uppercase white letters. The α-helix between strands E and F is shown in orange, and loops are shown in gray. Residues 41LYHY44 of the CC′ loop are labeled and highlighted in red, and their side chains are shown in stick representation. The CC′ and C′C″ loops and the N and C termini of the protein domain are indicated.