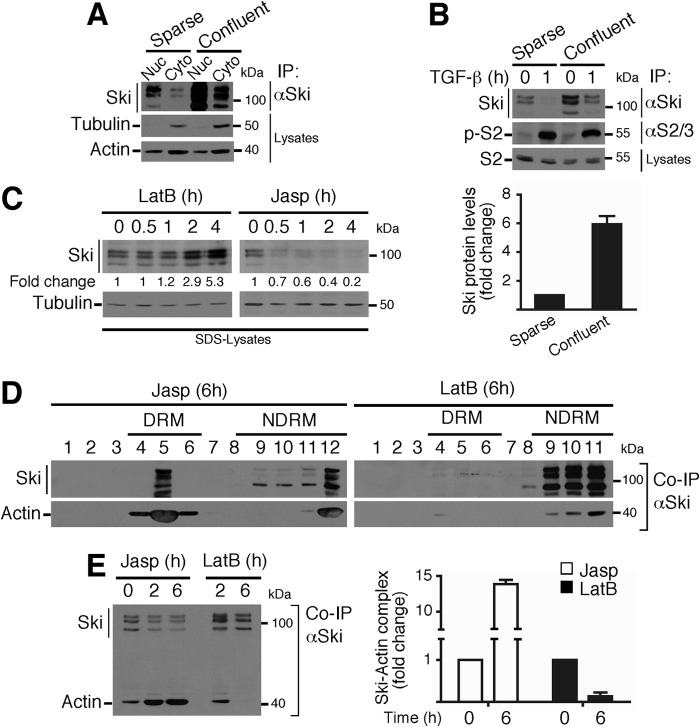
FIGURE 6.
Actin cytoskeleton dynamics modulate Ski protein stability. A, the nuclear (Nuc) and cytoplasmic (Cyto) fractions were obtained from sparse or confluent C9 cells, Ski protein was immunoprecipitated, and immunoblotting was performed for the indicated proteins from IP or cell lysates. B, sparse or confluent C9 cells were treated for 1 h with TGF-β. Ski and Smad2 proteins were immunoprecipitated, and immunoblotting was performed for the indicated proteins from IP or cell lysates (top panel). Bottom panel, densitometric analysis of Ski protein levels as -fold change in sparse versus confluent C9 cells. C, C9 cells were treated with 1 μm LatB or 0.5 μm Jasp for the indicated times, and immunoblotting was performed for the indicated proteins from SDS buffer lysates. The densitometric analysis of Ski protein levels is shown as -fold change over basal. D, C9 cells were treated for 6 h with 0.5 μm Jasp or 1 μm LatB, and DRMs and non-DRMs were obtained. Ski protein was immunoprecipitated, and immunoblotting was performed for the indicated proteins from co-IP. E, C9 cells were treated for 2 and 6 h with 0.5 μm Jasp or 1 μm LatB. Ski protein was immunoprecipitated, and immunoblotting was performed for the indicated proteins from co-IP (left panel). Right panel, densitometric analysis of Ski-actin complex levels as -fold change induced by Jasp or LatB. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments.