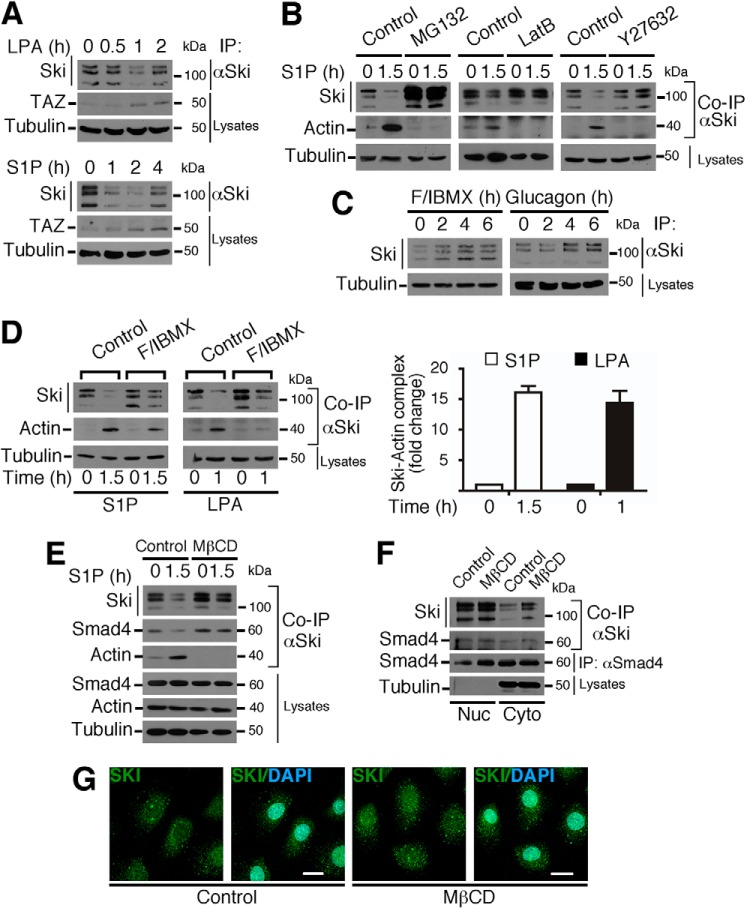
FIGURE 7.
GPCR signaling pathways differentially modulate Ski protein stability. A, C9 cells were stimulated with 1 μm LPA or 1 μm S1P for the indicated times. TAZ protein levels indicate LPA or S1P receptor activation. B, C9 cells were pretreated for 4 h without (Control) or with 25 μm MG132, 5 μm LatB, or 30 μm Y27632 and then stimulated for 1.5 h with 1 μm S1P. C, C9 cells were stimulated with a mixture of 1 μm F/100 μm IBMX mixture or with 2 μm glucagon for the indicated times. D, C9 cells were preincubated for 1 h in the absence (Control) or presence of a mixture of 2 μm F/100 μm IBMX and then stimulated for 1.5 h with 1 μm S1P or for 1 h with 1 μm LPA (left panel). Right panel, densitometric analysis of Ski-actin complex levels as -fold change induced by S1P or LPA. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. E, C9 cells were pretreated without (Control) or with MβCD for 4 h and stimulated with 1 μm S1P for 1.5 h. F, C9 cells were treated with MβCD for 3 h, and the nuclear (Nuc) and cytoplasmic (Cyto) fractions were obtained. In A–F, Ski protein was immunoprecipitated, and immunoblotting was performed for the indicated proteins from IP or cell lysates. G, C9 cells were treated with MβCD for 3 h, and endogenous Ski protein was detected by immunofluorescence. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars = 20 μm.