Figure 3.
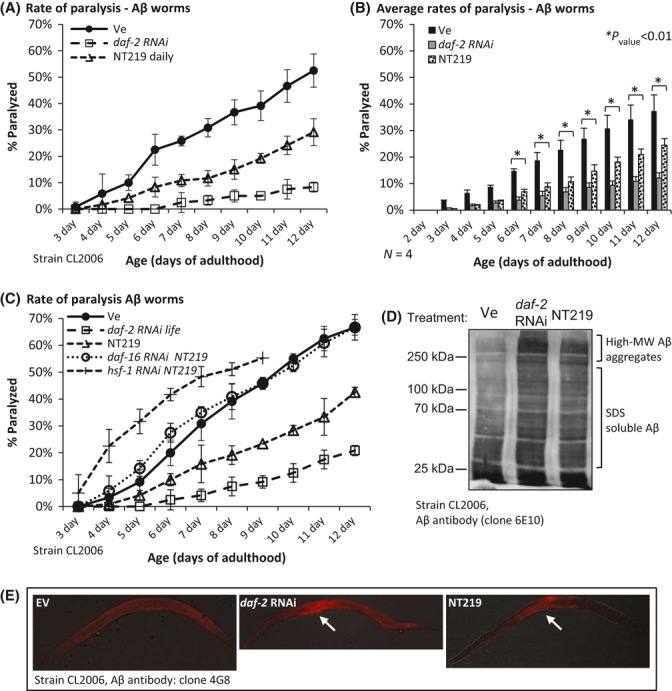
Protection from Aβ-mediated proteotoxicity by NT219. (A) CL2006 worms were cultivated on EV bacteria and treated with either 600 μm NT219 or the vehicle on days 1 and 2 of adulthood. The worms were placed on plates which supplemented daily with NT219 or the vehicle. Rates of paralysis were scored daily from day 3 to day 12 of adulthood. NT219 significantly reduced the rate of paralysis within the worm population (triangles) compared with the control group (black circles). daf-2 RNAi (open squares) provides more efficient protection compared with NT219. (B) Four independent repeats of the experiment described in A. (C) The knockdown of daf-16 (open circles) or hsf-1 (diamonds) by RNAi completely abolished the protective effect of NT219. (D) Similarly to daf-2 RNAi, NT219 treatment resulted in Aβ hyperaggregation as revealed by WB analysis of high-speed supernatants of CL2006 worms which were treated with the vehicle (Ve), NT219 or with daf-2 RNAi. (E) Immunofluorescence using an Aβ antibody indicates that IIS reduction by either NT219 or daf-2 RNAi leads to the accumulation of Aβ in the center of the worm.
