Figure 4.
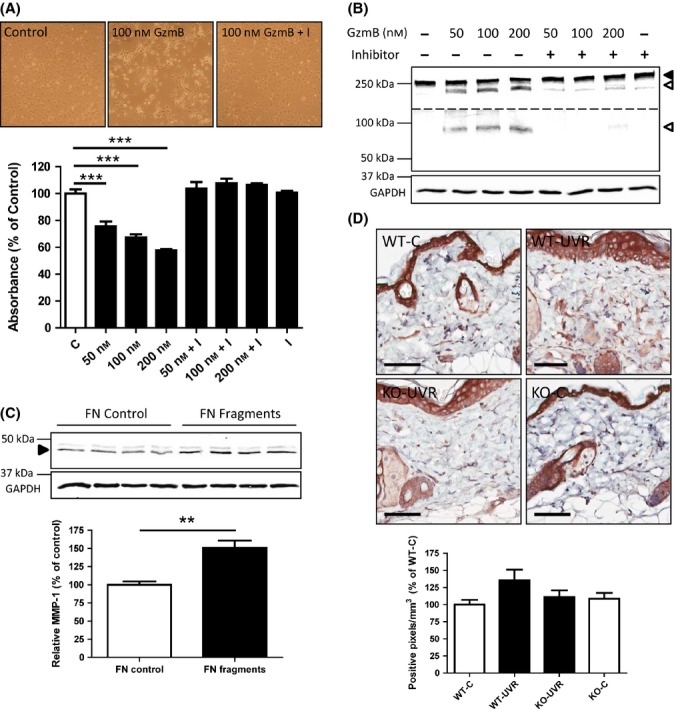
GzmB causes fibroblast detachment and fibronectin fragmentation in vitro, and GzmB-mediated FN fragments induce MMP-1 expression in fibroblasts. (A) Mouse fibroblasts plated overnight in complete medium were treated with the indicated concentrations of GzmB ± Inhibitor (I; 50 μm) for 7 h (in serum-free conditions). Adherent cells were assessed by MTS assay after washing once in PBS to remove nonadherent cells (mean ± SEM from quadruplicate wells; ***P < 0.001 Dunnett's multiple comparison). (B) Supernatants collected from (A) were assayed for fibronectin by Western blot. Closed arrowhead = full-length fibronectin; open arrowhead = fibronectin fragments. Although the same blot, the dotted line represents sections presented at different brightness/contrast so that fragments can be clearly observed at different kDa. (C) Primary fibroblasts were added to GzmB-mediated FN fragments, and MMP-1 release was assayed in the supernatants after 20 h by Western blot. GAPDH probed from cell lysates of the same wells served as loading controls. Results are presented as a percentage of intact fibronectin control (mean ± SEM from quadruplicate wells, **P < 0.01 t-test). (D) Dorsal skin sections from mice were stained with MMP-1 antibody, and intensity of staining in the dermis (excluding hair follicles) was measured by detecting the number of positive pixels above a set threshold, normalized to area. Results are expressed as a percentage of wild-type control (WT-C) (mean ± SEM). Scale bars = 60 μm.
