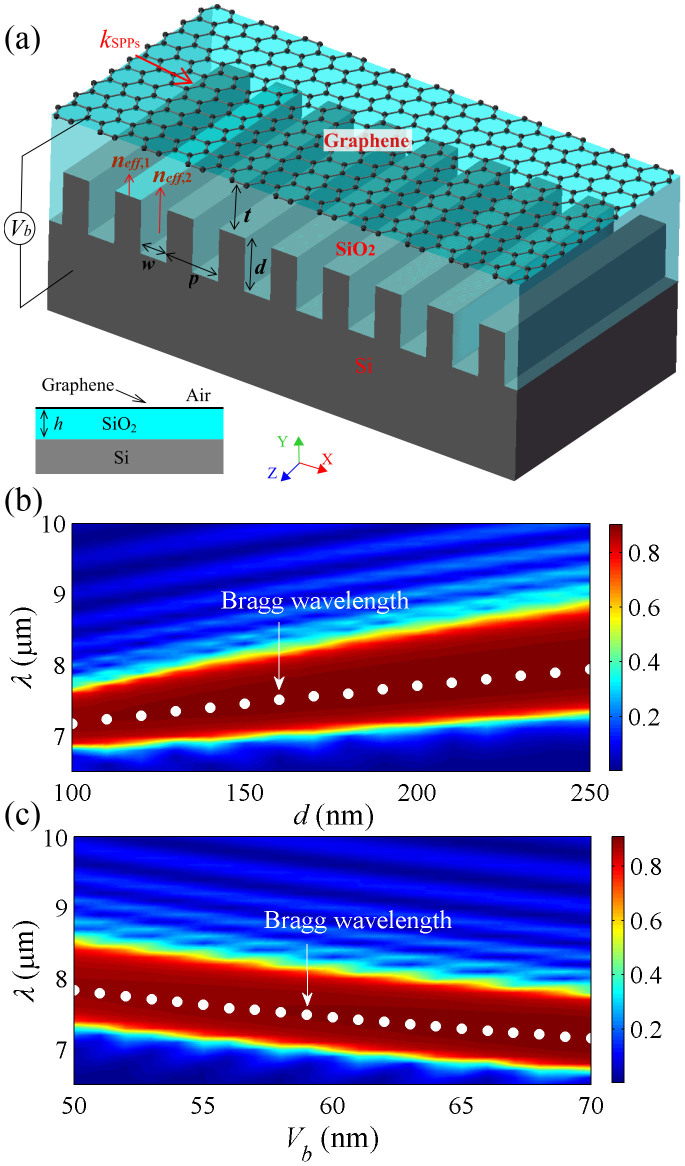
Figure 1. Schematic and reflectivity of the graphene Bragg grating.
(a) Schematic illustration of the graphene-based plasmonic Bragg grating structure. The surface conductivity of the graphene monolayer on silica (SiO2) can be tuned through an external gate voltage (Vb). The silicon (Si) substrate has a groove grating structure with period p, width w and depth d. t denotes the distance between the graphene and Si substrate. The inset shows a basic graphene-SiO2-Si structure with a SiO2 layer thickness h. (b) shows the reflectivity as a function of wavelength λ and grating groove depth d for a constant voltage Vb = 60 V and (c) as a function of wavelength λ and applied gate voltage Vb for a constant depth d = 150 nm. The other parameters are set as t = 100 nm, p = 2w = 40 nm, T = 300 K and μ = 20000 cm2V−1s−1. In the FEM simulations, the number of grating periods is 16 and SPP modes in graphene are excited from the left as indicated by the red arrow. The white circles represent the theoretical results for the Bragg grating operating wavelength obtained by solving Eq. (5).