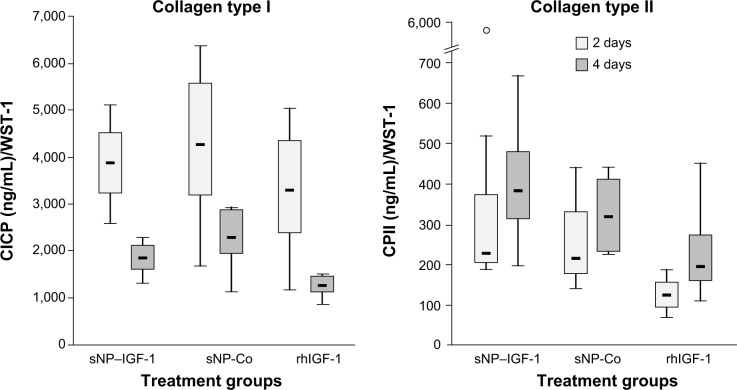
Figure 5.
Effect of IGF-1-coupled nanoparticles on chondrocytes grown in a monolayer for 2 and 4 days.
Notes: Chondrocytes were isolated from the hyaline cartilage of patients (n=3) undergoing primary total knee joint replacement and were cultured in a monolayer (1×105 cells per well in a 24-well plate). Cells were suspended in serum-free medium supplemented with rhIGF-1-coupled nanoparticles (sNP–IGF-1; 12.5 μg/mL particle suspension =50 ng/mL rhIGF-1), control particles (sNP-Co; 12.5 μg/mL particle suspension =50 ng/mL NH2), and rhIGF-1 (50 ng/mL). No medium change was conducted. After 2 and 4 days, CICP (osteogenic marker) as well as CPII (chondrogenic marker) were quantified in the cell supernatant by means of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data were normalized by division with WST-1 absorption values. Boxes denote interquartile ranges, horizontal lines within the boxes denote medians, and whiskers denote minimum and maximum values. Analysis of variance post hoc-LSD was conducted (there were no significant differences between 2 and 4 days of incubation nor between the 3 different treatments).
Abbreviations: CICP, procollagen type I; CPII, procollagen type II; LSD, least significant difference; sNP, silica nanoparticles; sNP-Co, control nanoparticles; WST-1, water-soluble-tetrazolium salt; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; rhIGF-1, recombinant human IGF-1.