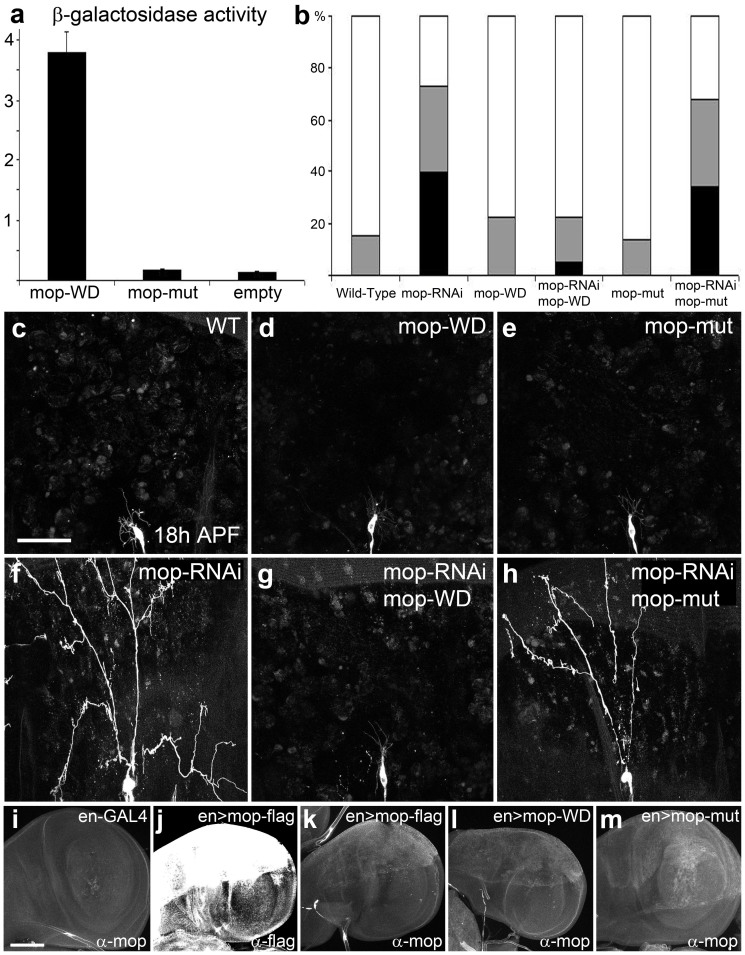
Figure 3. An interaction between Shrub and Mop is required for pruning.
(a) A Yeast-two-hybrid assay detects an interaction between Shrub (bait) and Mop Bro-domain. Wild-type Mop Bro-domain (mop-WD) binds to Shrub whereas the mutant Bro-domain (mutations in I201D and V205D) (mop-mut) does not bind. These tests were repeated four times, error bars indicate the standard deviations from the mean of triplicate measurements. (b) Quantification of pruning defect for the in vivo mop rescue experiments, Black = severing defect, Gray = clearance defect. White = wild-type pruning. N = 48, 40, 40, 37 and 44, respectively. ppk-GAL4 > CD8::GFP shows wild-type pruning at 18 h APF (c) as do ddaC neurons expressing UAS-mop-WD (wild type Bro-domain), n = 40 (d) or UAS-mop-mut (point mutation I201D and V205D in the Bro-domain), n = 37 (e). ddaC neurons expressing mop-RNAi show a robust disruption in severing at 18 h APF, n = 48 (f). mop-RNAi combined with UAS-mop-WD completely rescues the RNAi severing defect, n = 40 (g). mop-RNAi along with UAS-mop-mut results in a robust severing defect, n = 44 (h). Imaginal wing disc expressing of UAS-mop constructs under the control of en-GAL4 (i–m). Comparison between Flag and Mop antibody (j–k) Detection by Mop antibody shows similar levels of expression of UAS-mop-WD and UAS-mop-mut (l–m). Scale bar = 50 μm.