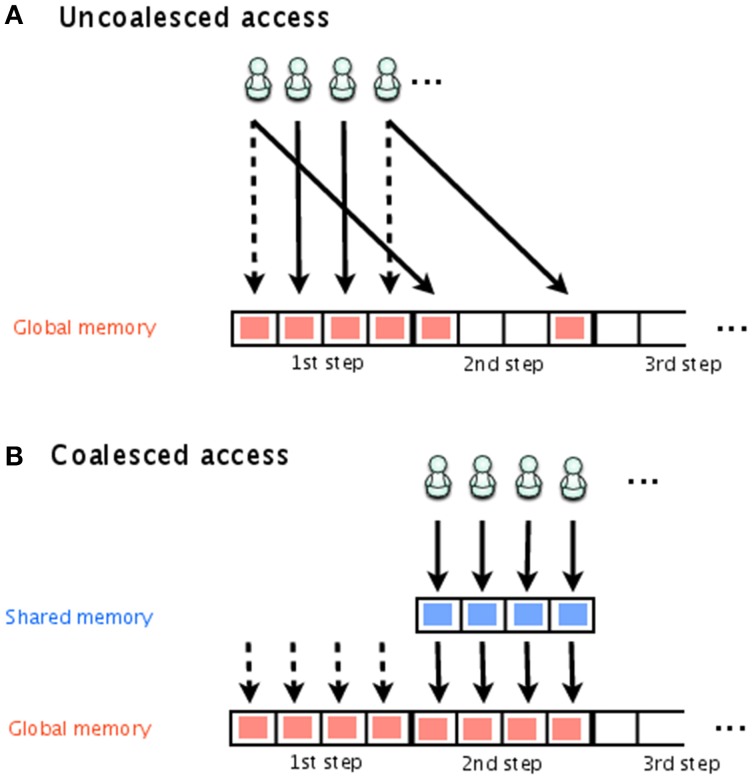
Figure 2.
Uncoalesced and coalesced access to global memory. Stick figures indicate the threads that access global memory for the storage of the simulation results. In (A), threads 1 and 4 have already finished storing their results for the first step and are attempting to store the results for the second step; threads 2 and 3 are attempting to store their results for the first step. This is an example of uncoalesced access. In (B), shared memory is used to temporarily store the simulation results, which are later transferred together to global memory. This is an example of coalesced access.