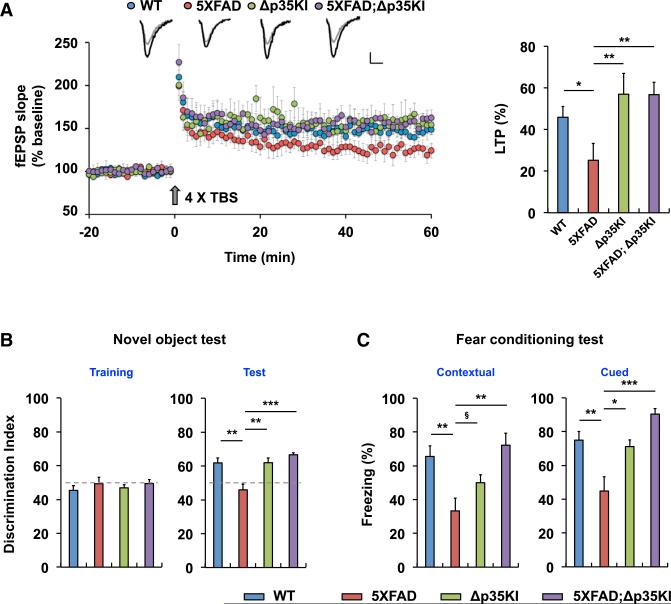
Figure 6. Inhibition of p25 Generation Rescues Synaptic Dysfunction and Cognitive Impairment in 5XFAD Mice.
(A) LTP was induced by 4× TBS at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses. Sample traces represent fEPSPs at 1 min before (gray) and 1 hr after (black) TBS. Scale bars, 0.5 mV and 10 ms. Right: the magnitude of LTP was calculated by comparing the average slopes of fEPSPs during the last 10 min of recordings with those recorded before stimulation. WT: 146.0% ± 5.1%, 8 slices from 5 mice; 5XFAD: 125.2% ± 8.1%, 7 slices from 5 mice; Δp35KI: 157.0% ± 10.1%, 5 slices from 3 mice; 5XFAD;Δp35KI: 156.8% ± 5.9%, 5 slices from 3 mice, p < 0.01 by ANOVA.
(B) Novel-object test with WT, Δp35KI, 5XFAD, and 5XFAD;Δp35KI mice. Right: discrimination index for novel-object recognition (WT: 61.8 ± 2.8, n = 8; 5XFAD: 45.9 ± 3.5, n = 7; Δp35KI: 61.9 ± 2.8, n = 6; 5XFAD;Δp35KI: 66.6 ± 1.3, n = 9, p < 0.001 by ANOVA).
(C) Contextual and cued FC tests with WT, Δp35KI, 5XFAD, and 5XFAD;Δp35KI mice. Left: contextual FC (WT: 65.6% ± 6.4%, n = 10; 5XFAD: 33.3% ± 7.6%, n = 12; Δp35KI: 50.0% ± 4.7%, n = 11; 5XFAD;Δp35KI: 72.2% ± 7.0%, n = 7, p < 0.05 by ANOVA). Right: cued FC (WT: 75.0% ± 5.0%, n = 10; 5XFAD: 44.9% ± 8.3%, n = 12; Δp35KI: 71.2% ± 3.9%, n = 11; 5XFAD;Δp35KI: 90.5% ± 3.1%, n = 7, p < 0.01 by ANOVA).
§p = 0.08, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by Tukey's post hoc analysis; error bars ± SEM. See also Figure S6.